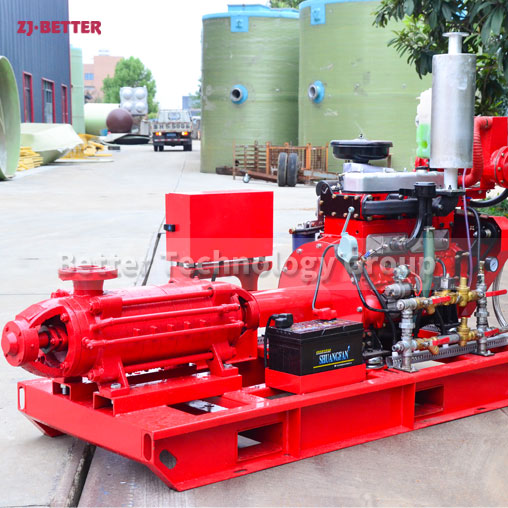
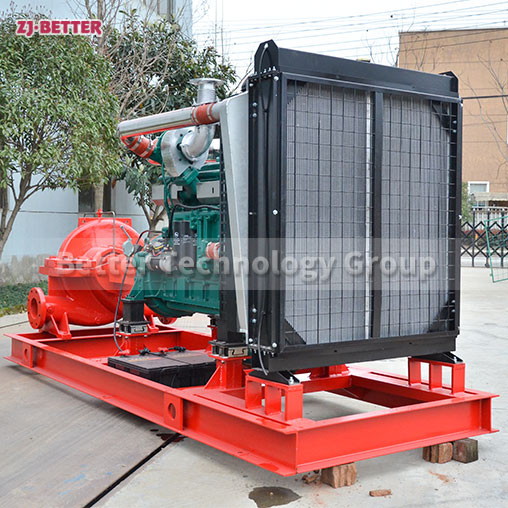
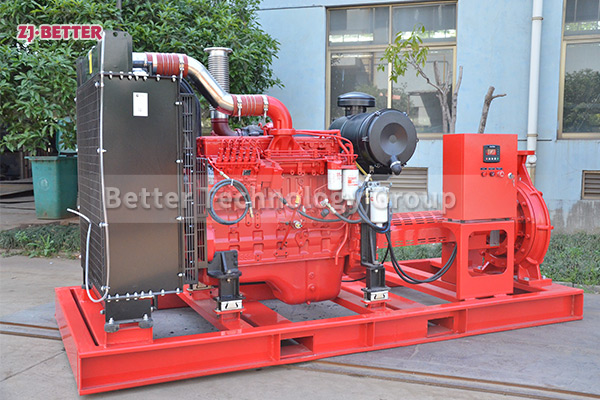
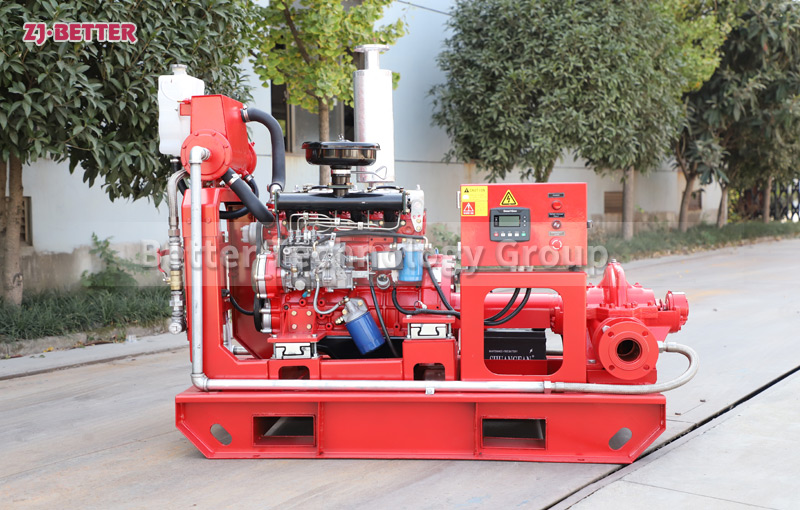
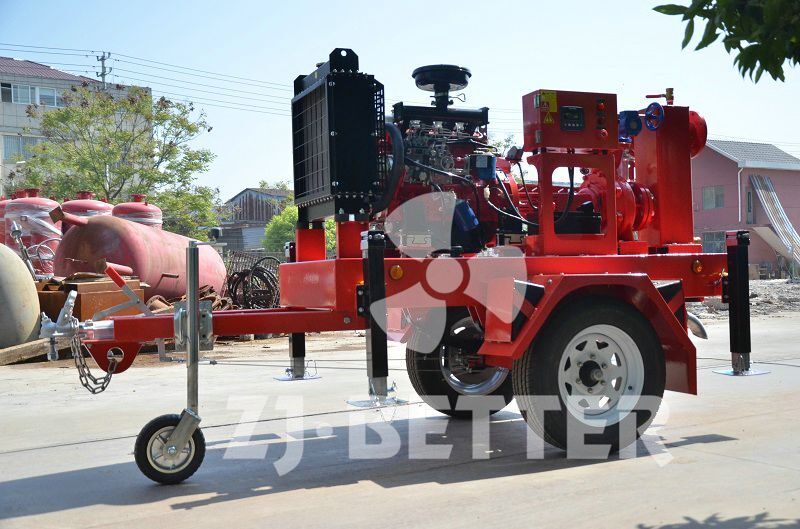
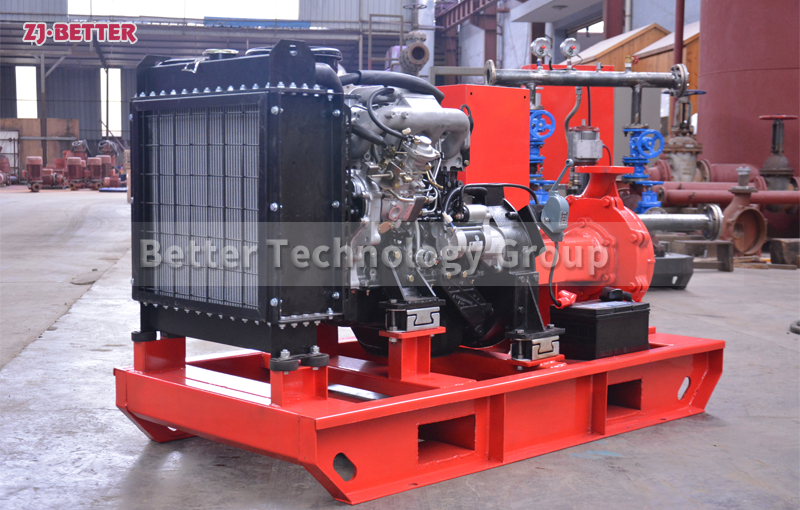
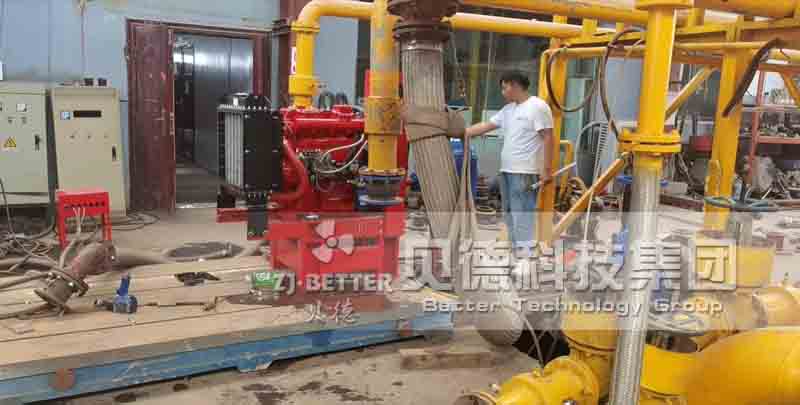
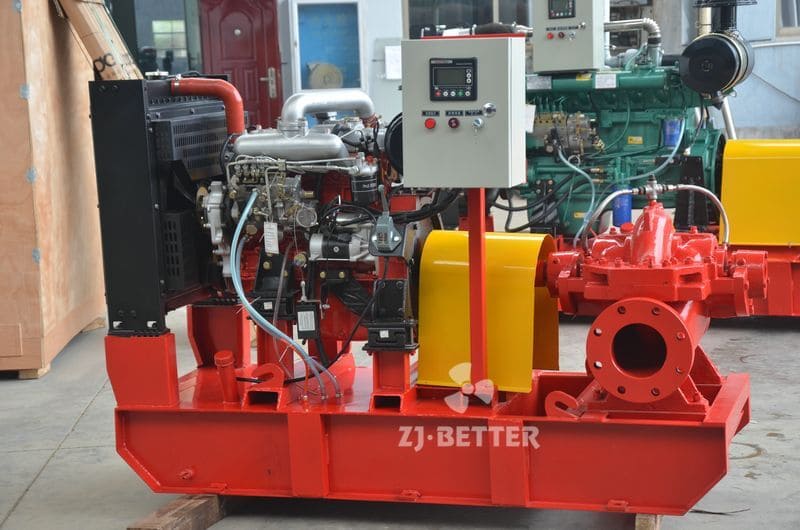
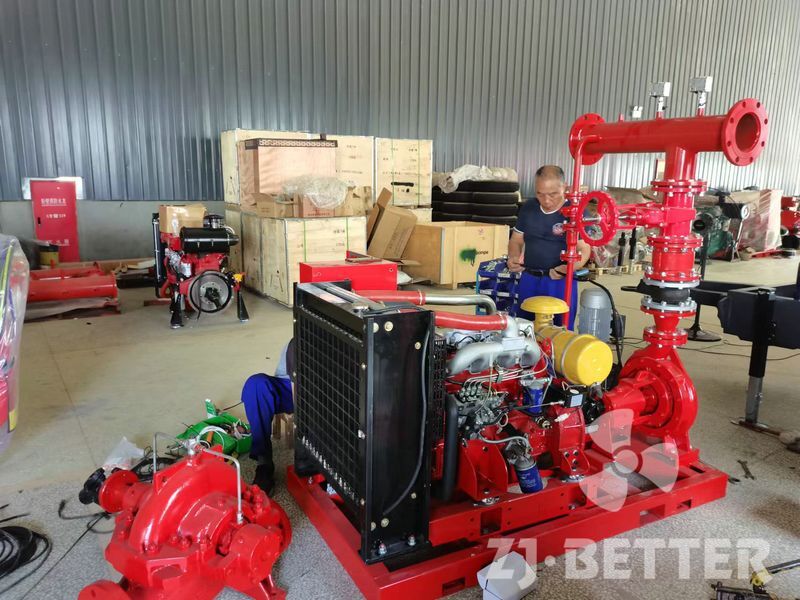
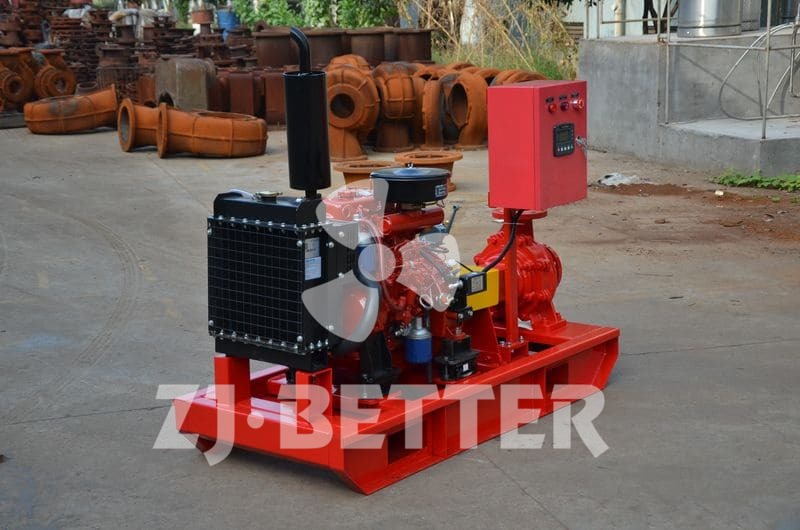
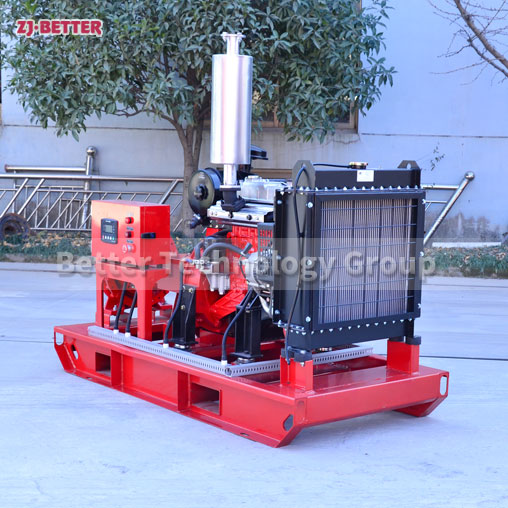
How does a diesel multistage pump work?
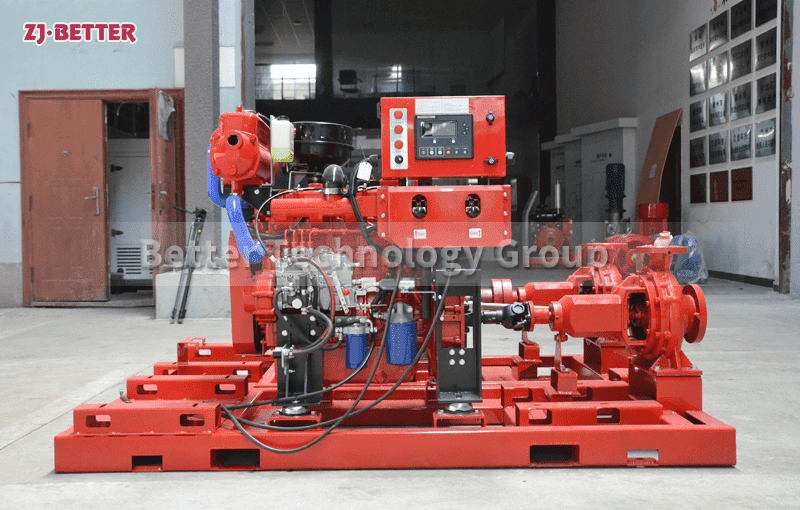
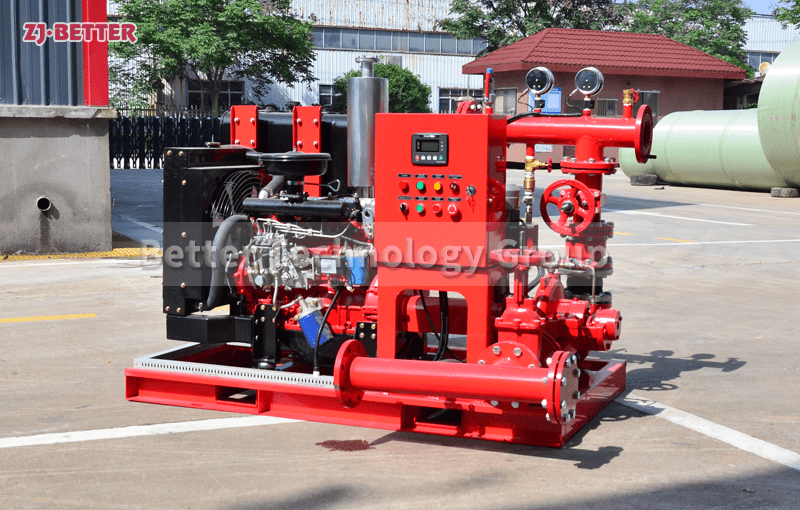
Multistage pumps are designed to transfer cleaning liquids through multiple impellers in series instead of one, and are typically used in installations that require high lift. High pressure applications can be achieved by mounting the impellers on the same shaft of the multistage pump or on opposite shafts parallel to each other for higher flow rates. They are mainly used for energy saving and different range of flow/head situations.
How does a multistage pump work?
Multistage pumps work in the connected stage. The process begins with liquid entering a chamber at suction line pressure and then leaving at elevated pressure before entering the next chamber. This process can be continued multiple times, and the more chambers a multistage pump has, the higher the achievable pressure. The number of industries and sectors that can benefit from multistage pumps is virtually endless, and there are many examples where they can be applied.