Home » Diesel engine fire pump » Features of Split Case Diesel Engine Fire Pump
Features of Split Case Diesel Engine Fire Pump
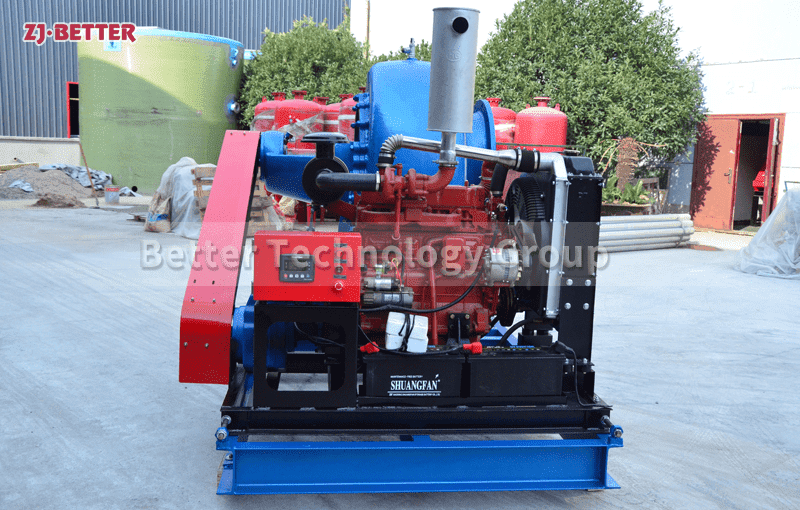
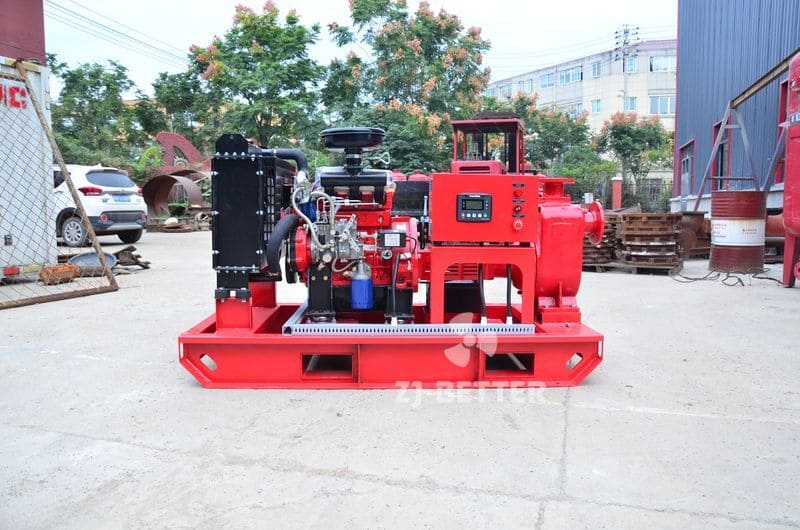
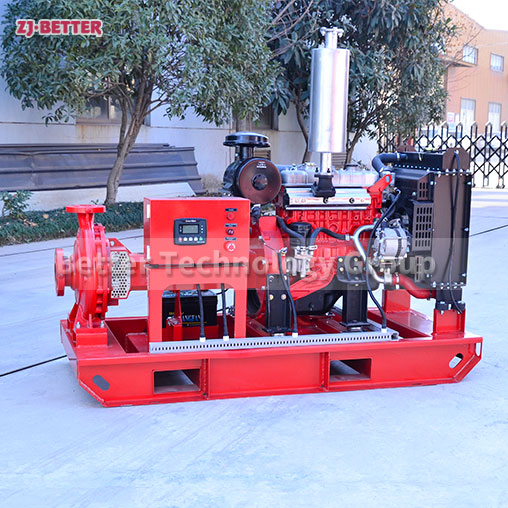
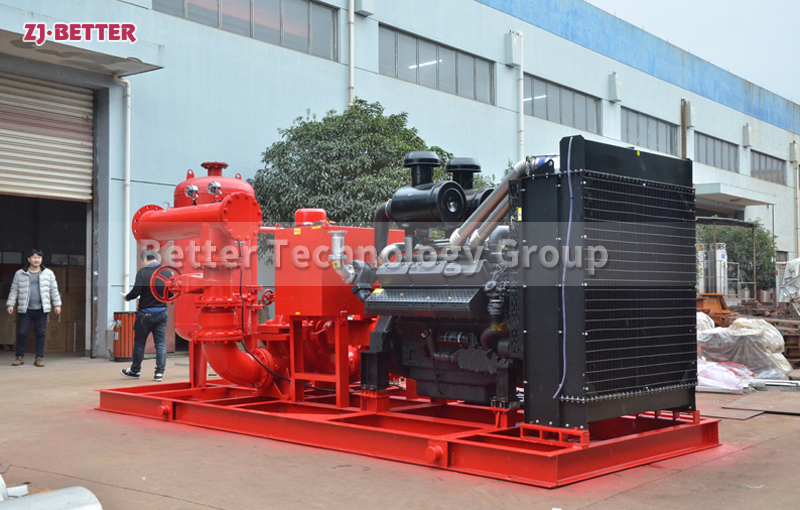
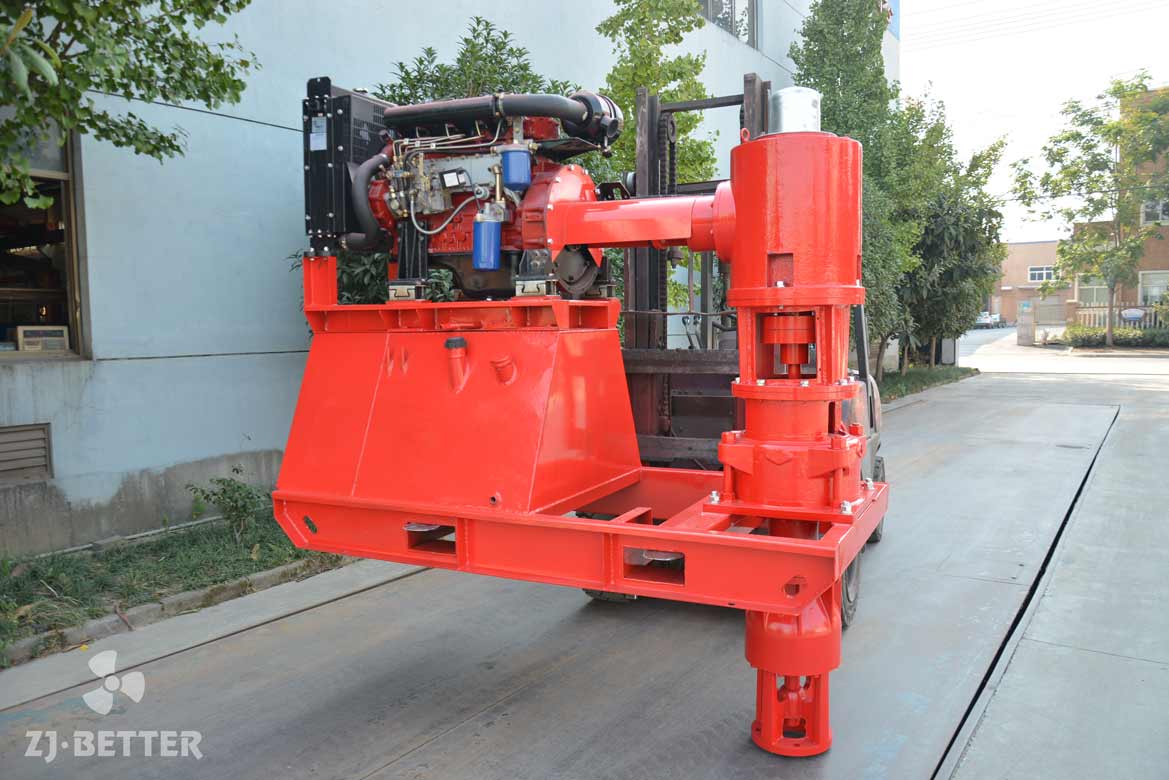
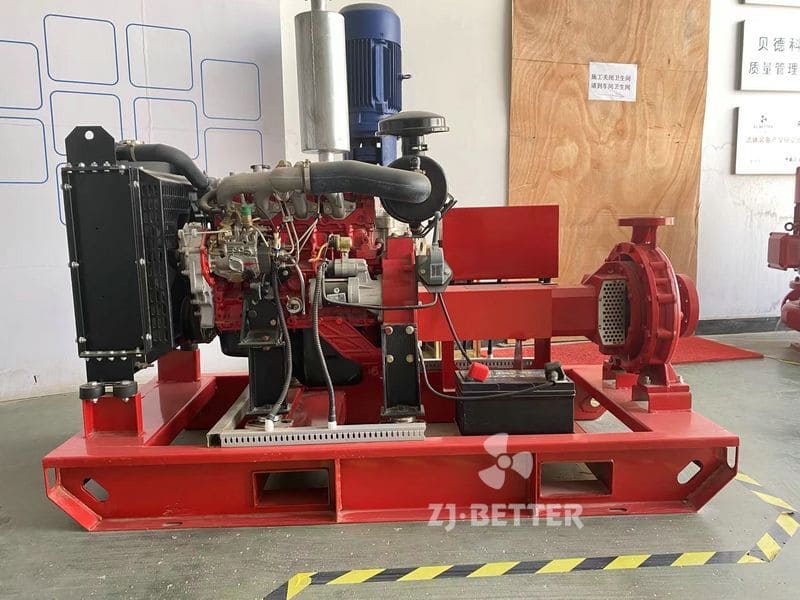
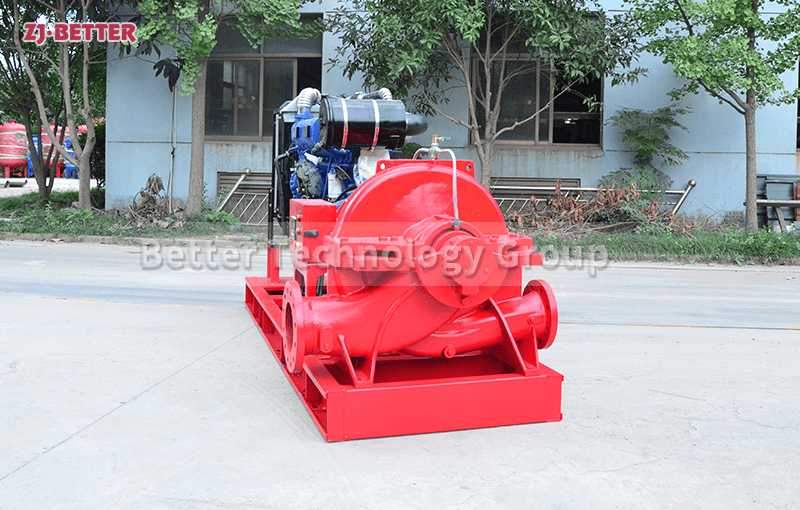
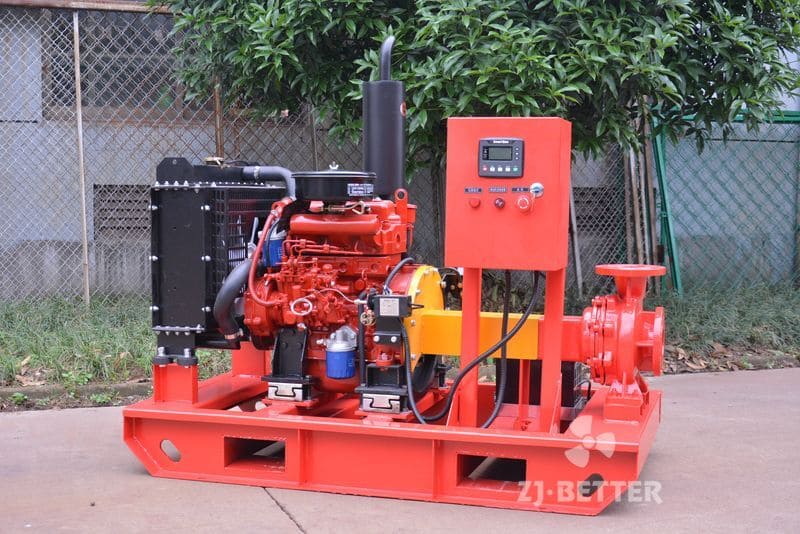
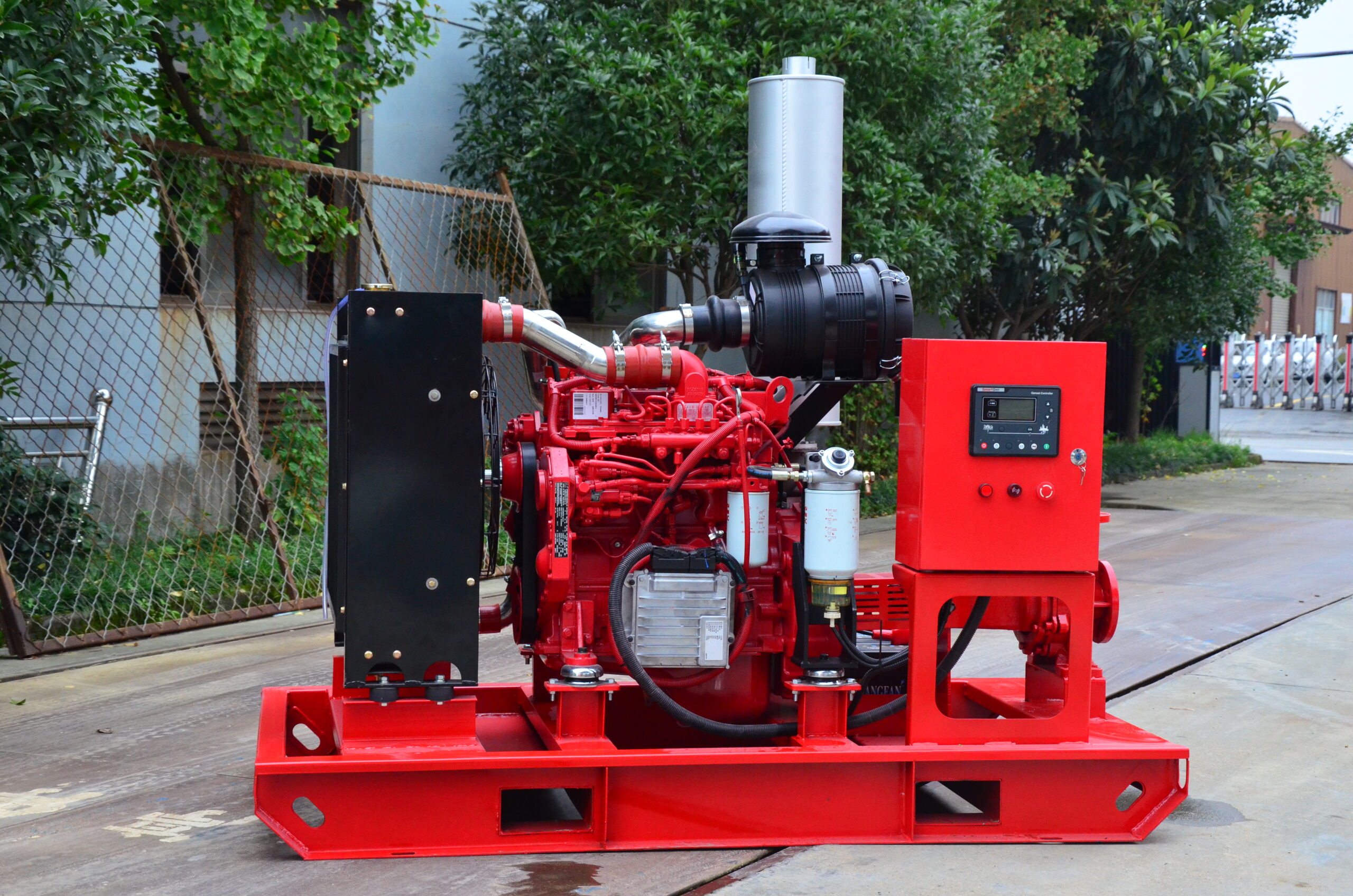
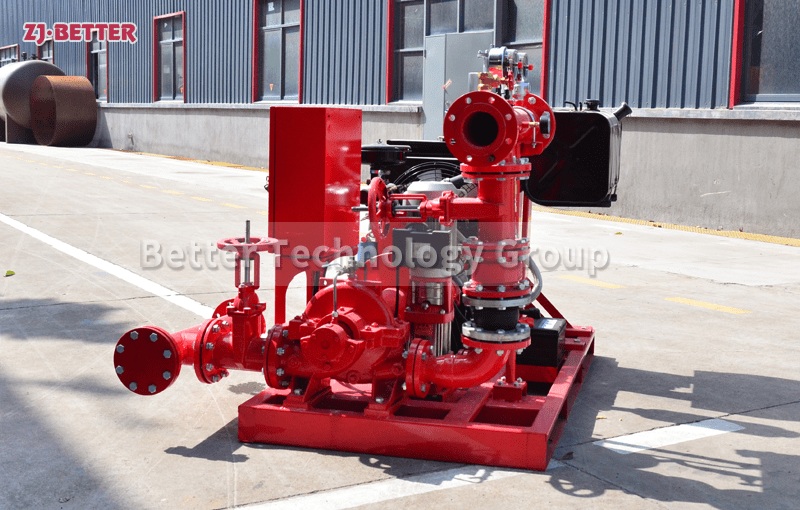
Split case diesel engine fire pump combines the features of a split case fire pump with the reliability and independence of a diesel engine-driven system. This configuration is commonly used in applications where a dependable source of power is crucial to maintain fire protection capabilities during power outages or in remote locations. Here are the key features of a split case diesel engine fire pump:
Contact US
Get Price
Share:
Content
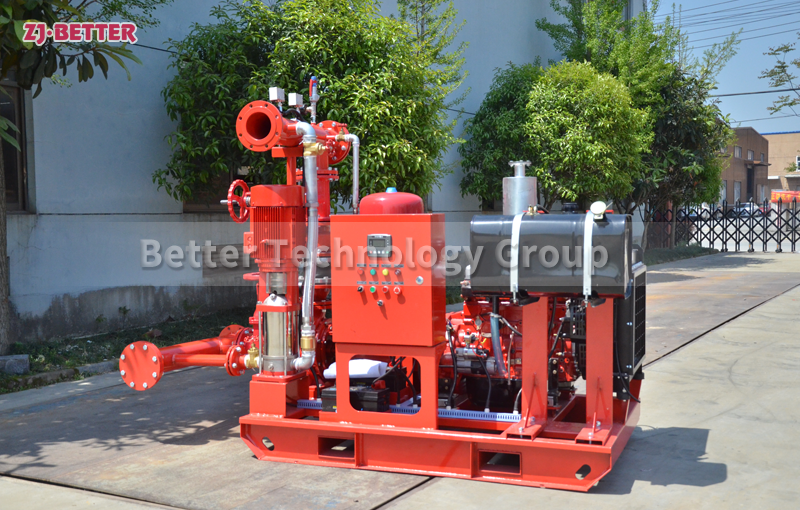
- Split Case Design: Like a standard split case fire pump, the casing of a split case diesel engine fire pump is horizontally split, allowing easy access to the internal components for maintenance and repairs.
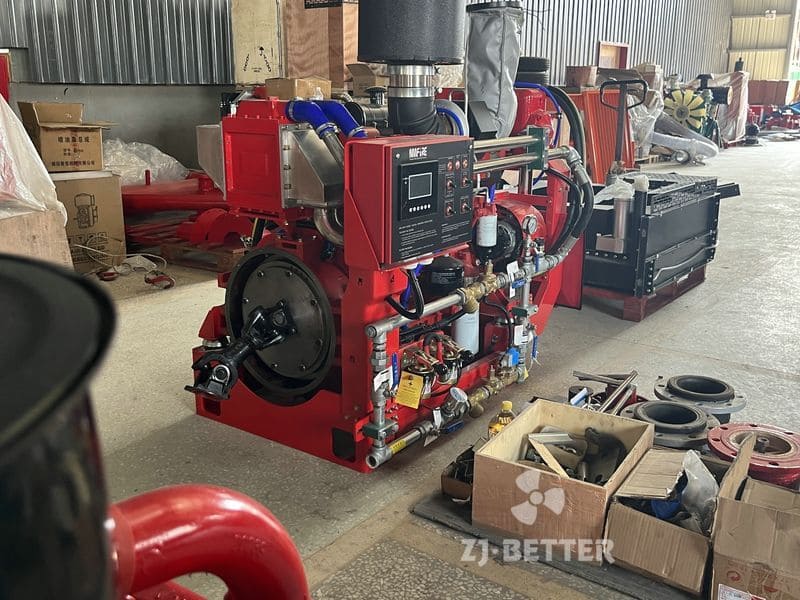
- Diesel Engine Driven: The pump is powered by a diesel engine, providing a reliable source of power that is independent of the electrical grid. Diesel engines are known for their robustness and ability to operate for extended periods without access to electricity, making them ideal for emergency fire protection situations.
- High Flow Capacity: Split case diesel engine fire pumps retain the high flow capacity characteristic of split case pumps, enabling them to deliver a substantial volume of water to the fire protection system.
- Bi-Directional Impeller: The pump is equipped with a bi-directional impeller, eliminating the need to consider the rotation direction during installation.
- Suction and Discharge Connections: The pump set has designated suction and discharge connections, drawing water from a source and delivering it to the fire protection system.
- Control Panel and Monitoring: A control panel is included to monitor the diesel engine and pump operation. It may feature automatic start/stop functions, engine monitoring, fault detection, and system status indicators.
- Diesel Fuel Tank: A diesel fuel tank is integrated into the system to provide a sufficient fuel supply to the diesel engine during emergency operations.
- Redundancy and Reliability: Split case diesel engine fire pumps are designed for high reliability and may be part of a redundant fire protection system, where multiple pumps
Inquiry
More Diesel engine fire pump