In modern urban safety infrastructure and industrial fire protection systems, fire pumps play a pivotal role in ensuring timely and reliable water supply. The performance expectations—high efficiency, rapid response, operational stability, and ease of maintenance—are increasingly demanding. In particular, scenarios such as remote industrial sites, emergency rescue zones, construction sites, and temporary fire protection installations often expose the limitations of traditional centrifugal pumps. These pumps require manual priming, foot valves, and complex pipework, resulting in delayed startup and higher maintenance requirements. Self-priming pumps have emerged as an ideal solution to these challenges due to their unique operating principle and structural advantages.
The core principle of a self-priming pump relies on retaining a small volume of liquid within the pump casing. Upon startup, this liquid interacts with incoming air, forming a vacuum that draws water from the source automatically—eliminating the need for manual priming. This feature ensures that the pump can operate immediately in fire emergencies, saving critical response time and significantly enhancing firefighting performance.
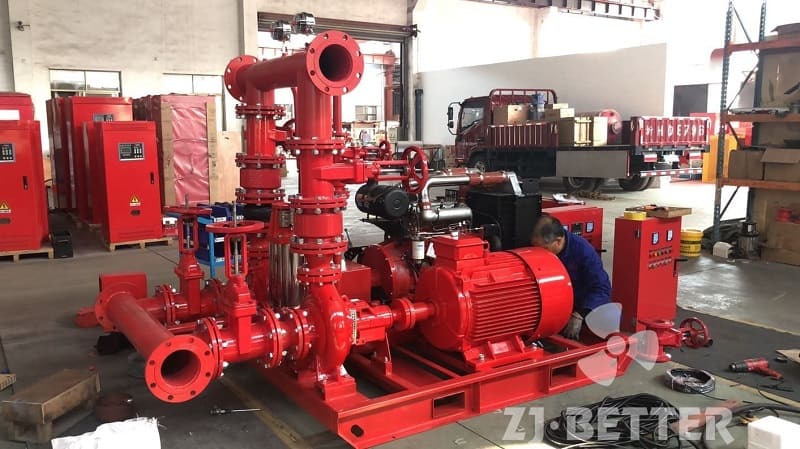
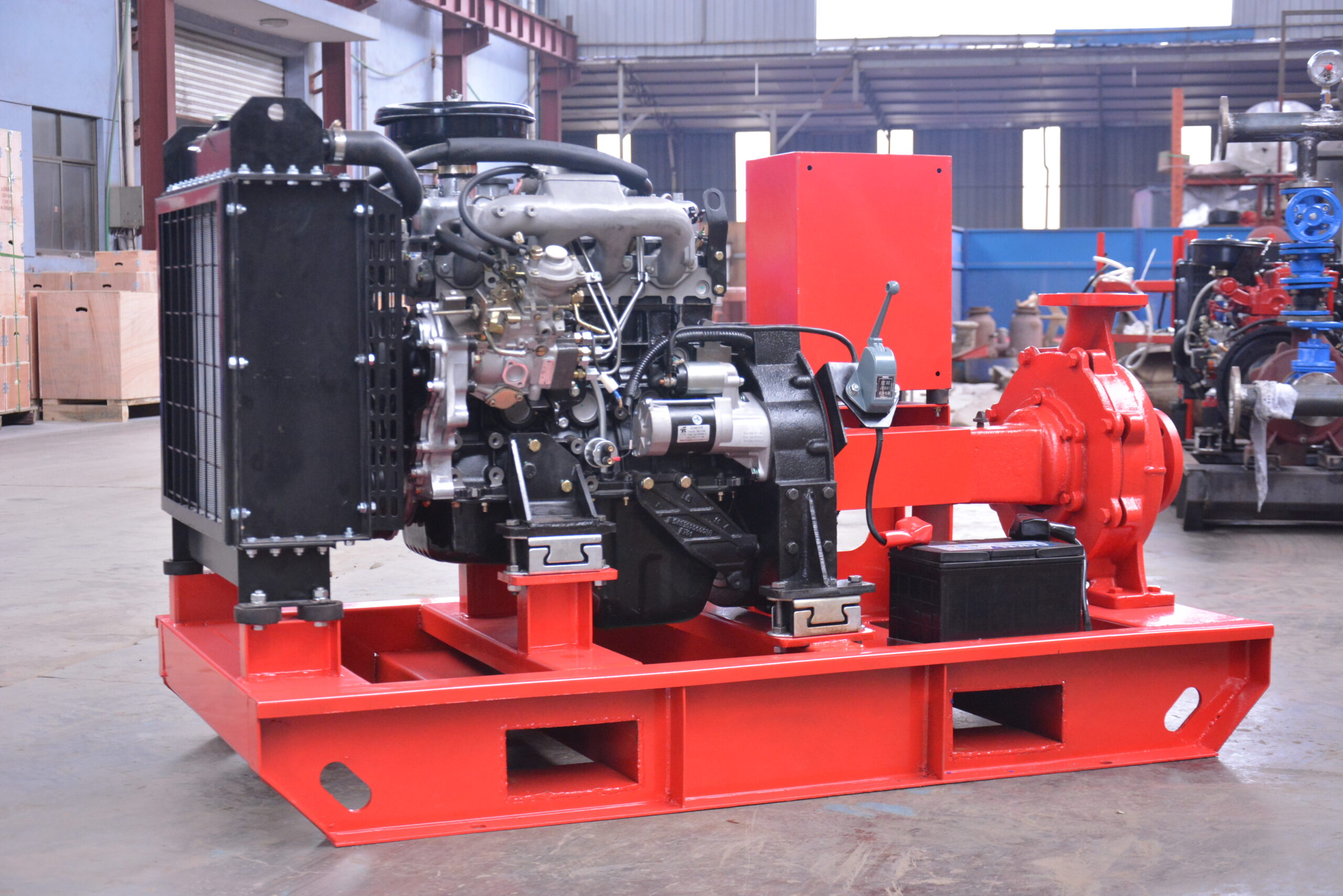
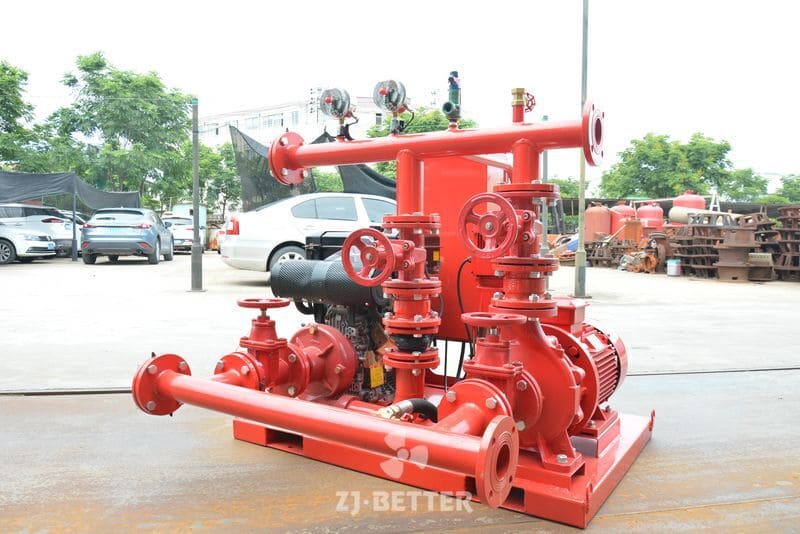
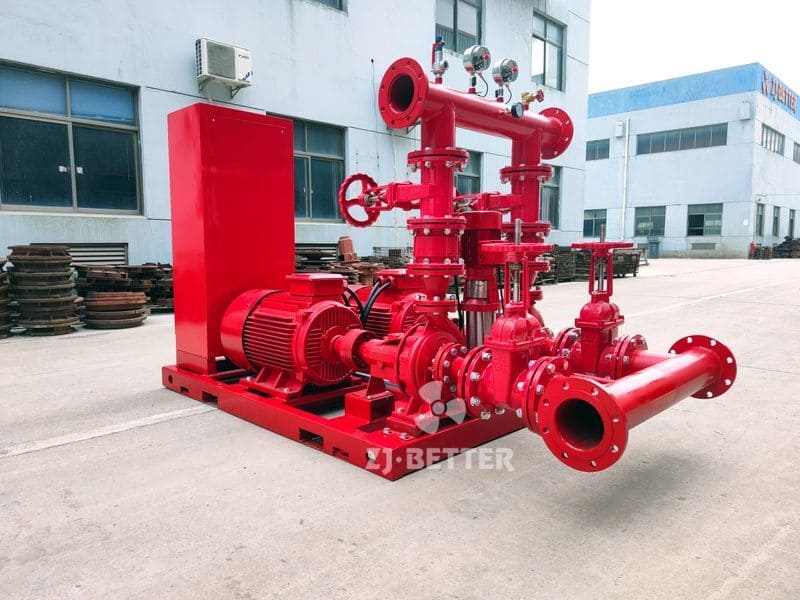
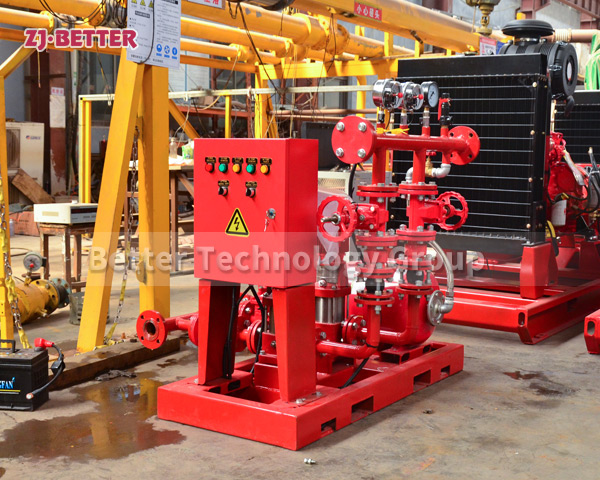
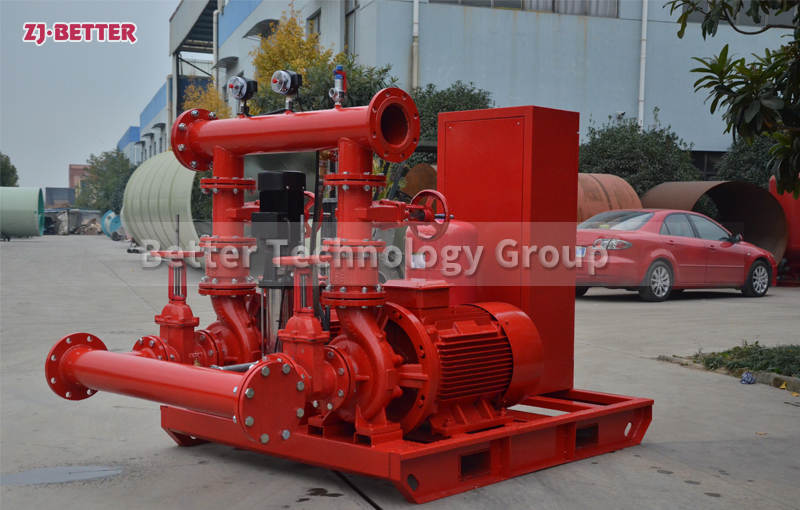
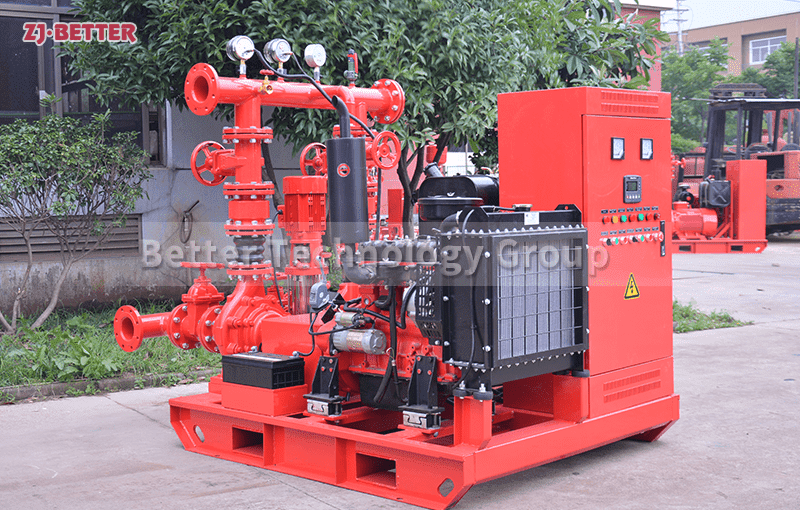
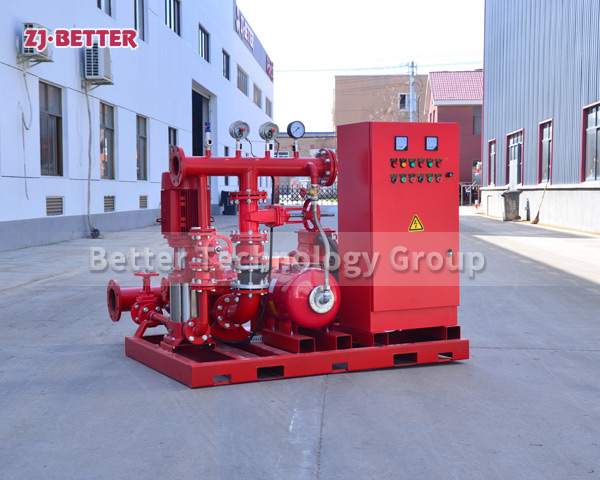
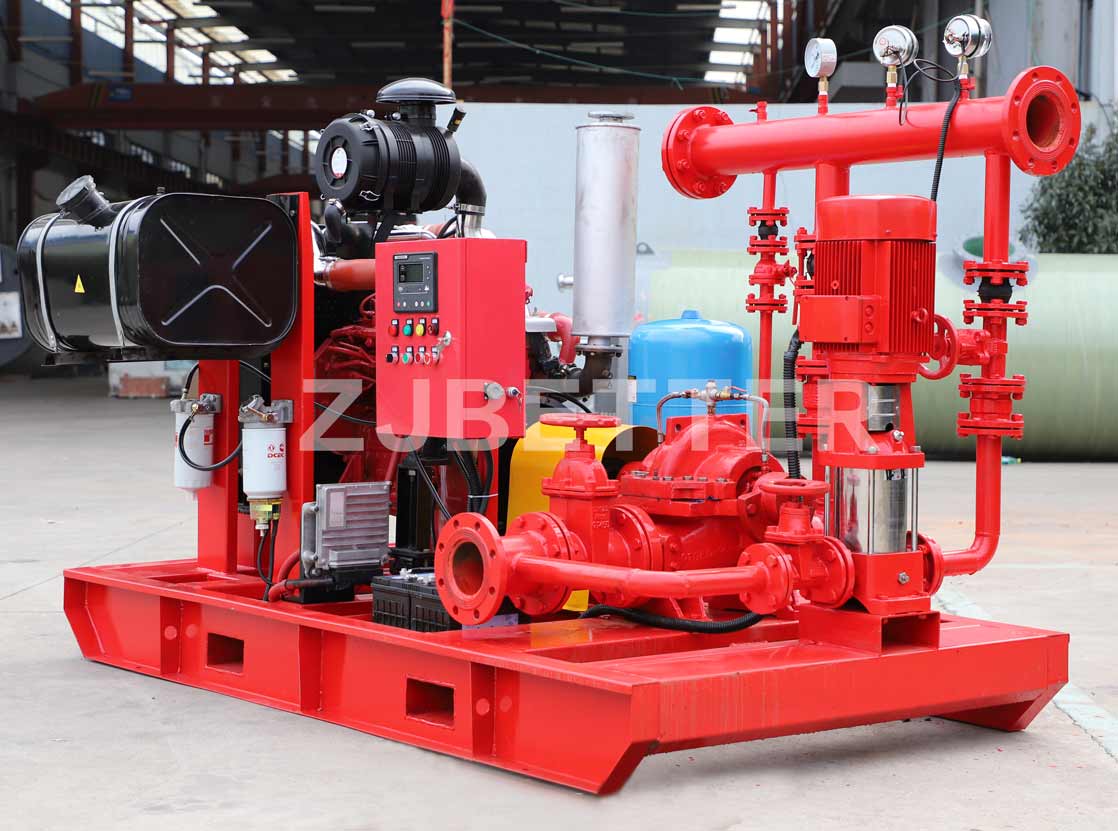
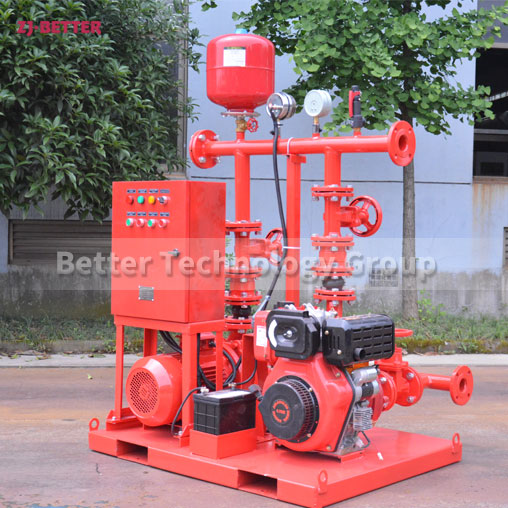
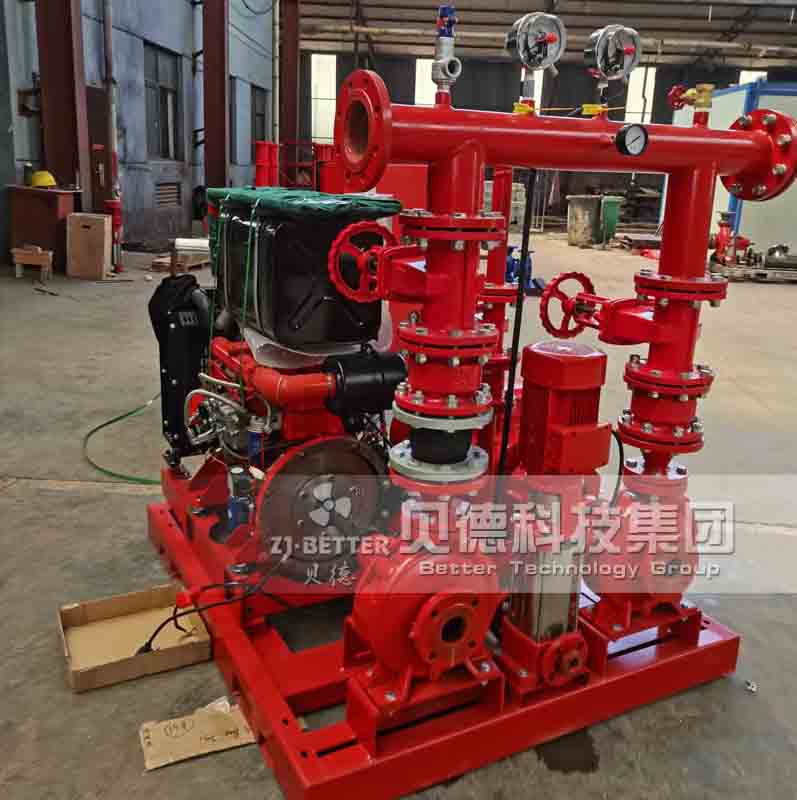
Structurally, high-efficiency self-priming pumps are typically constructed with integrated cast housings. The pump body is commonly made of high-strength cast iron or stainless steel, offering excellent resistance to corrosion and wear. These materials allow the pump to handle a wide range of liquids, including sediment-laden water, rainwater, wastewater, or fluid with solid content. The impeller is engineered with optimized hydraulic geometry to reduce turbulence losses, improve suction lift, and achieve higher head pressure. Furthermore, mechanical seals use advanced materials such as silicon carbide or fluororubber to provide superior sealing under harsh conditions, extending service life.
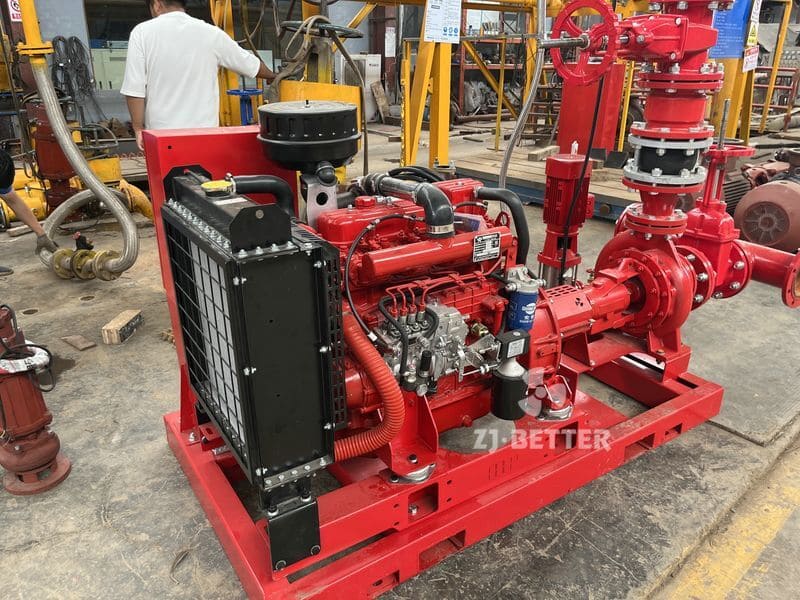
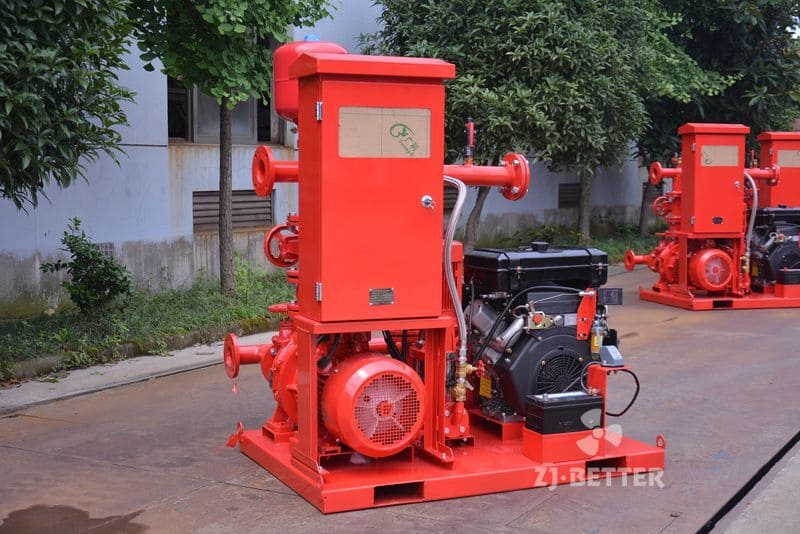
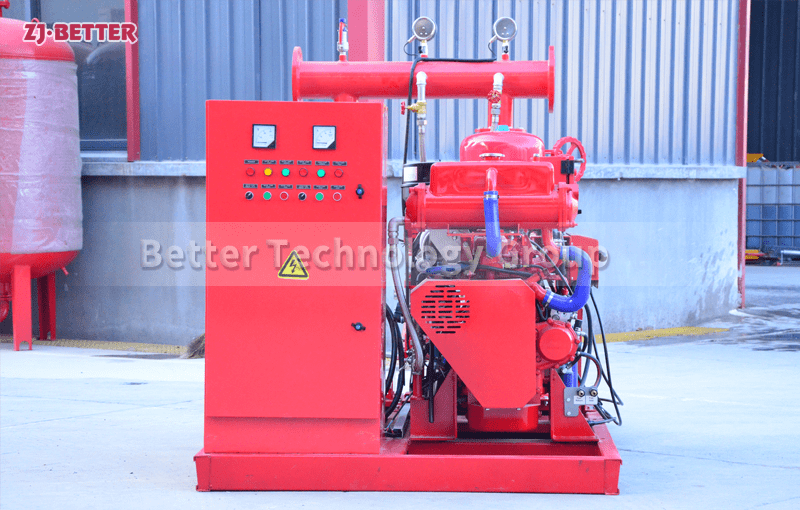
On the drive side, these pumps are coupled with high-efficiency motors compliant with national or international energy standards. Some models can also be configured with diesel engines, making them suitable for power-deficient or outdoor applications. In terms of automation, self-priming pumps can be integrated with fire control panels or PLC systems, supporting remote start/stop, automated diagnostics, dry-run protection, and real-time data monitoring. This increases the overall intelligence and reliability of the fire protection system.
From an installation perspective, self-priming pumps eliminate the need for foot valves and separate priming lines, reducing installation complexity and cost. The horizontal, compact design makes them easy to deploy in tight or irregular spaces. For maintenance, the quick-access cover design allows for convenient inspection and part replacement, minimizing downtime and maintenance expenditure.
In summary, high-efficiency self-priming pumps deliver a unique combination of automatic operation, fast response, compact design, durable construction, and wide applicability. These features make them indispensable in industrial fire protection, municipal systems, temporary pumping stations, water treatment plants, and even agricultural irrigation. As smart firefighting and energy-efficient infrastructure continue to evolve, self-priming pumps are poised to play a key role in the next generation of firefighting systems.