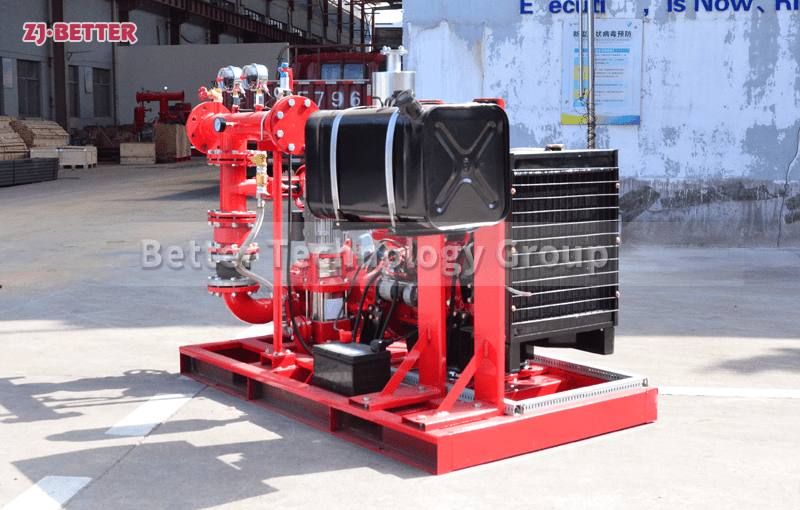
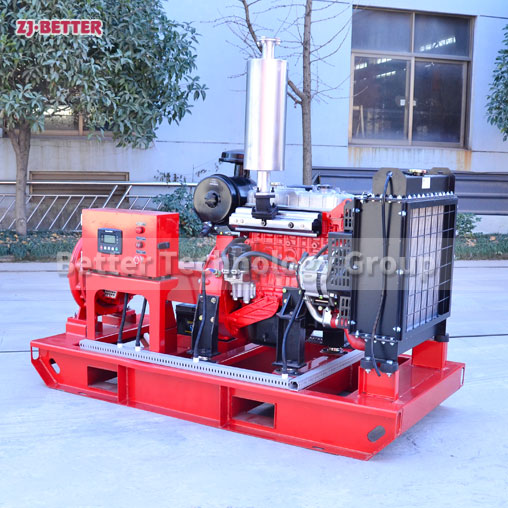
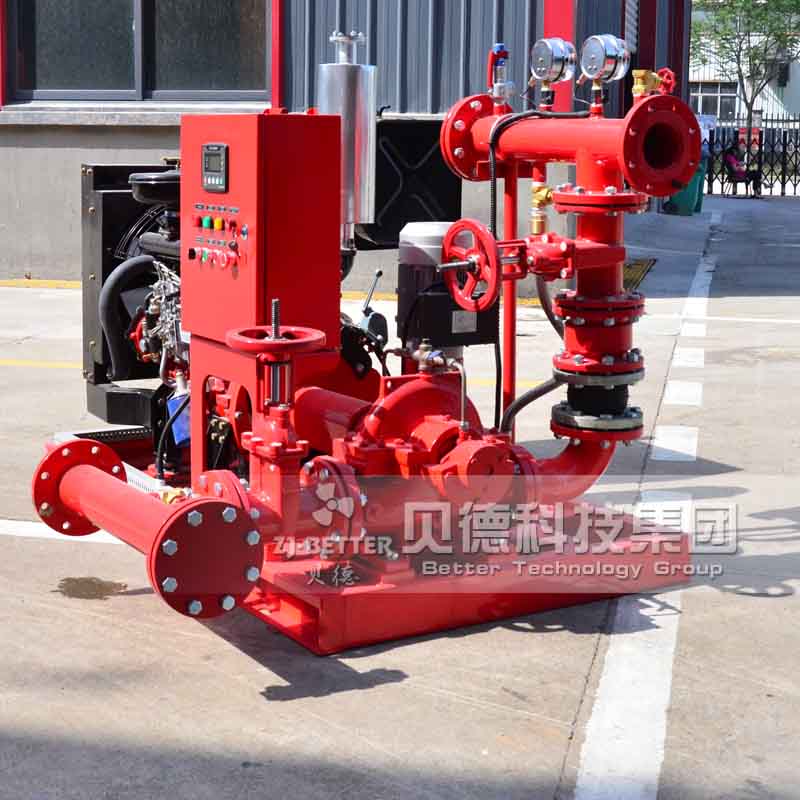
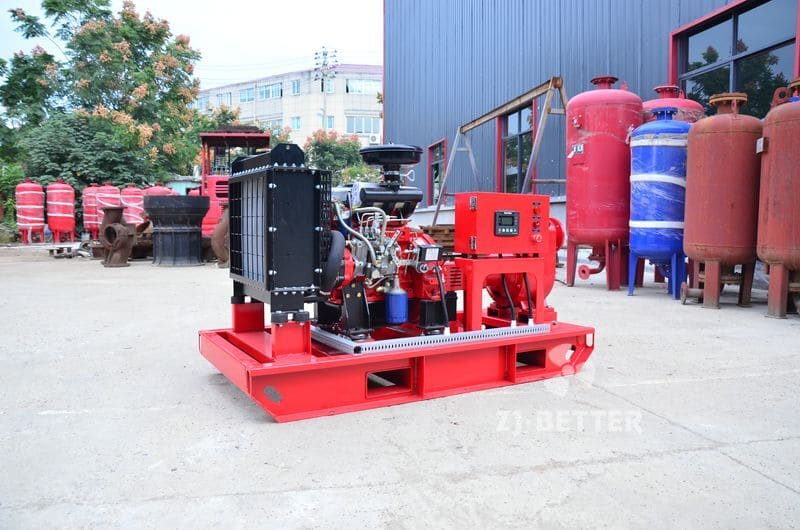
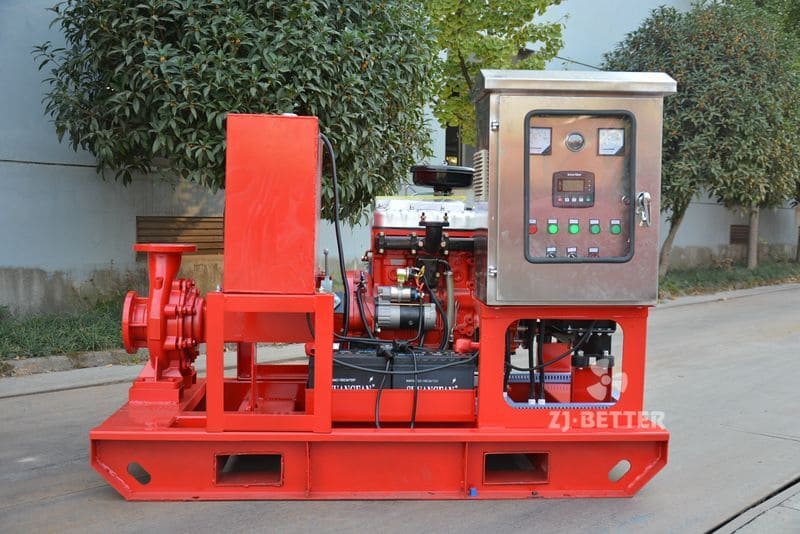
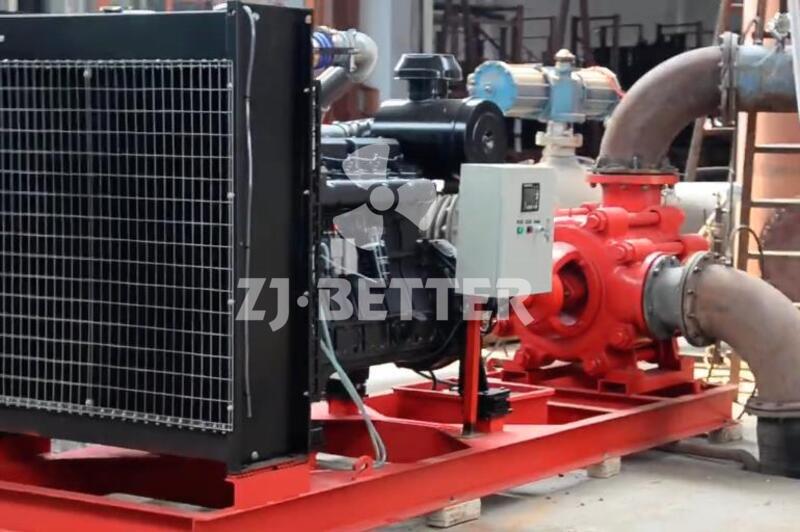
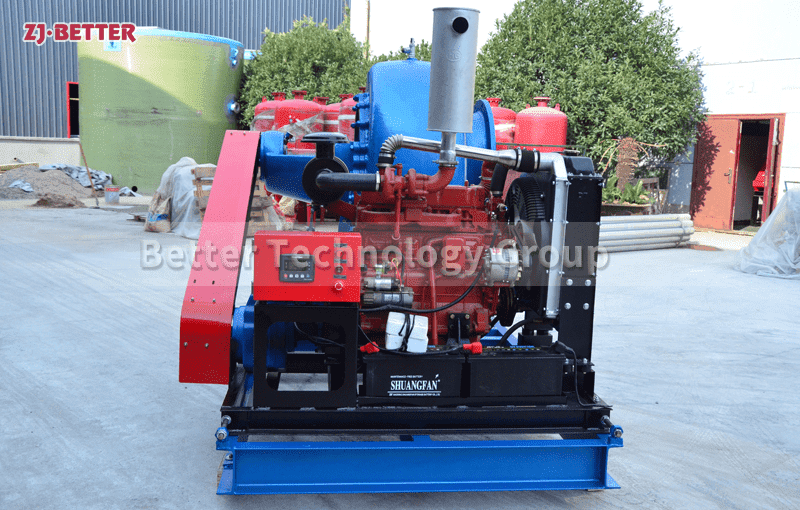
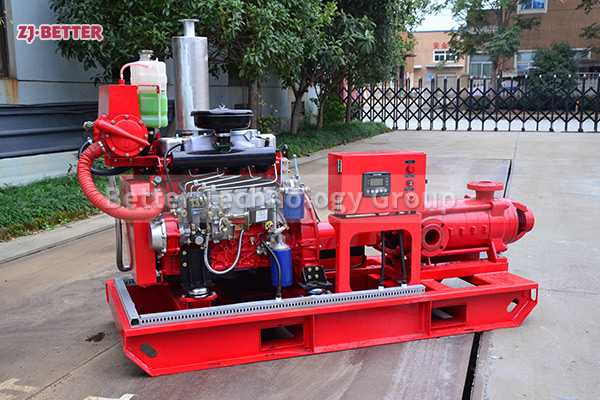
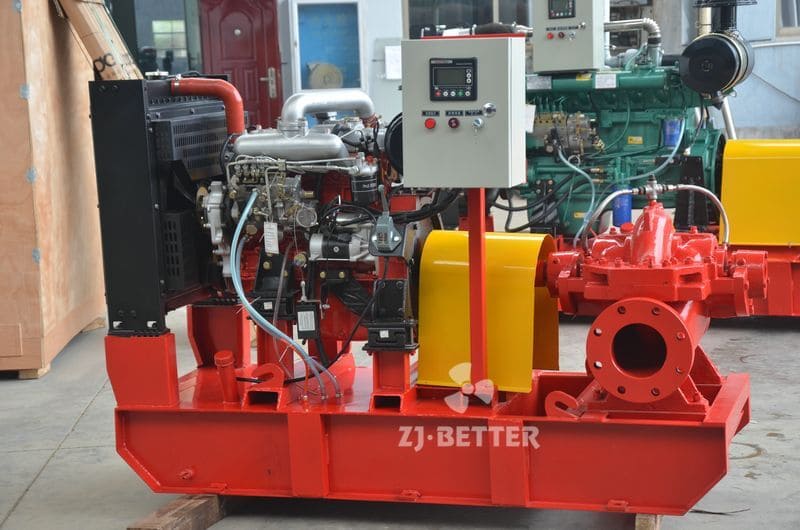
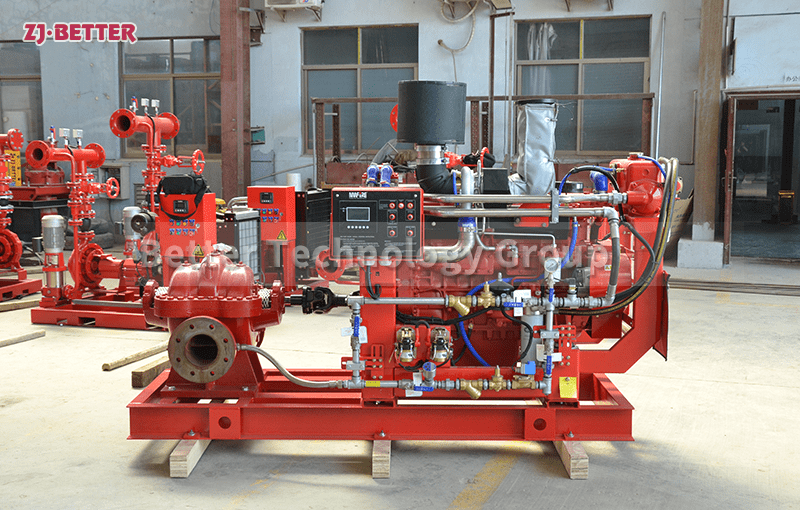
Diesel engine fire pump function description
It can be combined with electric pumps, jockey pumps, etc. to form an automatic water fire protection water supply system, and can be linked with the fire control center.
When the pump set receives the starting command, if the mains power is cut off, the automatic control cabinet of the diesel engine will immediately send a start signal to the starting motor of the pump set to start the motor to start the diesel engine at idle speed, and then gradually adjust the throttle to accelerate the diesel engine to the rated speed. . The control system will automatically monitor the operation of the diesel engine, such as the oil pressure, oil temperature, speed of the diesel engine, outlet pressure of the water pump, etc., and determine whether the diesel engine starts normally through automatic monitoring. If the start fails, the control system will send a restart signal, and if the three starts fail, the automatic control system will send a failure alarm. When the pump set receives a signal that the pressure of the pipeline network is restored or the mains power is restored to normal, the pump set will quickly slow down and stop automatically after monitoring the idle position for a period of time.
When the diesel engine fire pump is running, the crankshaft pulley is driven by the transmission belt to drive the water pump impeller and coolant to rotate. Under the action of its own centrifugal force, the coolant is thrown out along the blade to the edge of the impeller, and the coolant discharged by the impeller enters the extrusion chamber along the slit channel on the volute tangent to the impeller. Most of its speed energy is converted into pressure energy, which is then pressed into the water jacket of the cylinder block and cylinder head of the diesel engine. At this time, a low pressure or vacuum is formed at the inlet of the impeller due to the discharge of liquid, which generates a certain suction force on the water inlet of the water pump, and makes the coolant in the water tank be forced into the impeller inlet of the water pump through the water inlet pipe. The rotating impeller continuously sucks in and discharges coolant, forming a forced circulation in the cooling system.