How to Choose the Right Fire Pump for Your Building
Learn how to choose the ideal fire pump for your building by evaluating system demand, pump type, NFPA 20 compliance, and water supply conditions.
When it comes to protecting lives and property, selecting the correct fire pump for your building is critical. The right fire pump ensures adequate water flow and pressure to your fire protection system—especially when it matters most. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key factors to consider when choosing a fire pump, in compliance with NFPA 20 standards.
1. Identify the Fire Protection System Requirements
Start by understanding what your building needs in terms of fire protection. Are you supporting a sprinkler system, a standpipe system, or both? Each has different flow and pressure requirements:
-
Sprinkler Systems: Typically require lower pressure but consistent flow.
-
Standpipe Systems (for high-rise buildings) Often require higher pressure to overcome elevation.
Work with a fire protection engineer to determine your exact system demand in gallons per minute (GPM) and pressure in psi or bar.
2. Evaluate Water Supply Conditions
Your water supply source directly impacts your pump choice. Common sources include:
-
Municipal Water Supply: Requires analysis of static and residual pressure.
-
Storage Tank or Reservoir: Must consider suction lift and ensure positive pressure.
-
Well Systems: Often used in remote or rural areas and may need special pump types like vertical turbines.
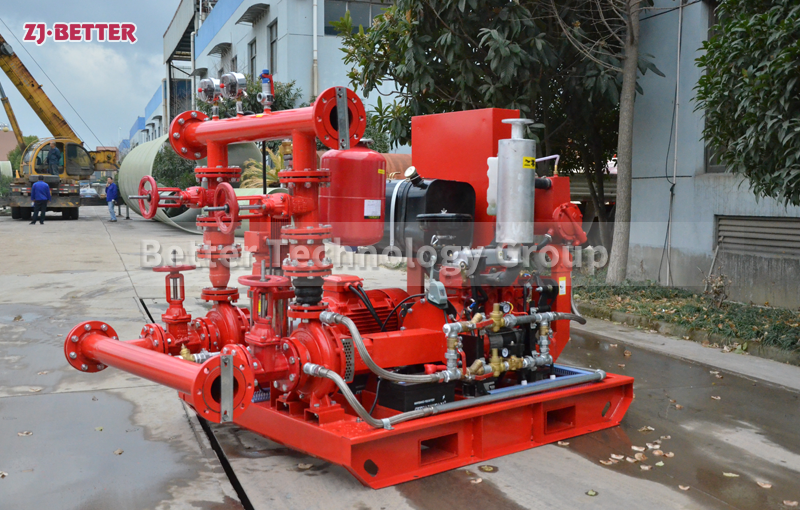
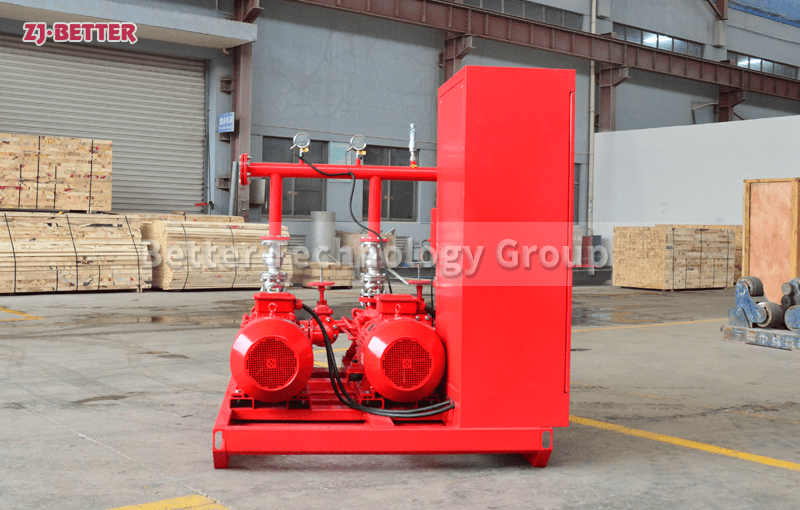
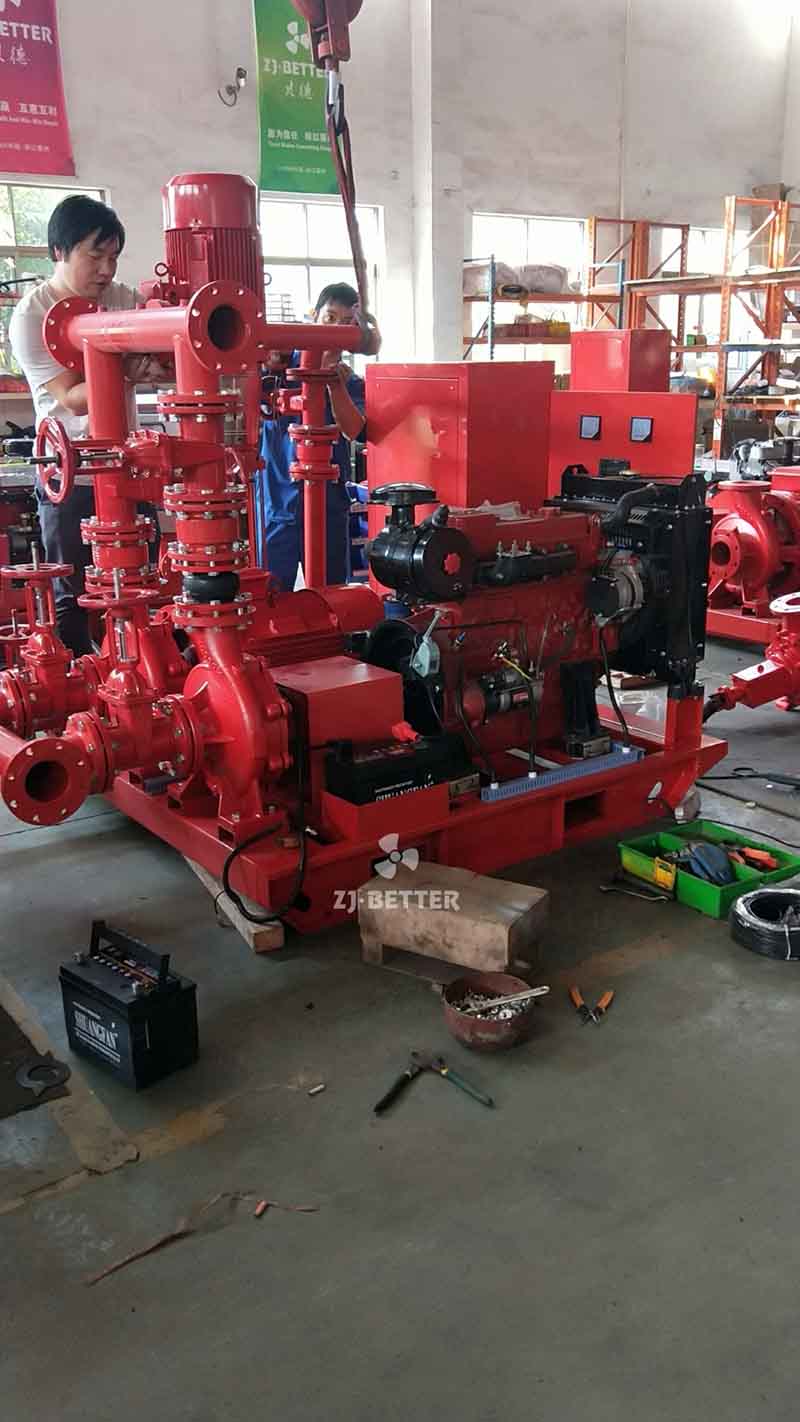
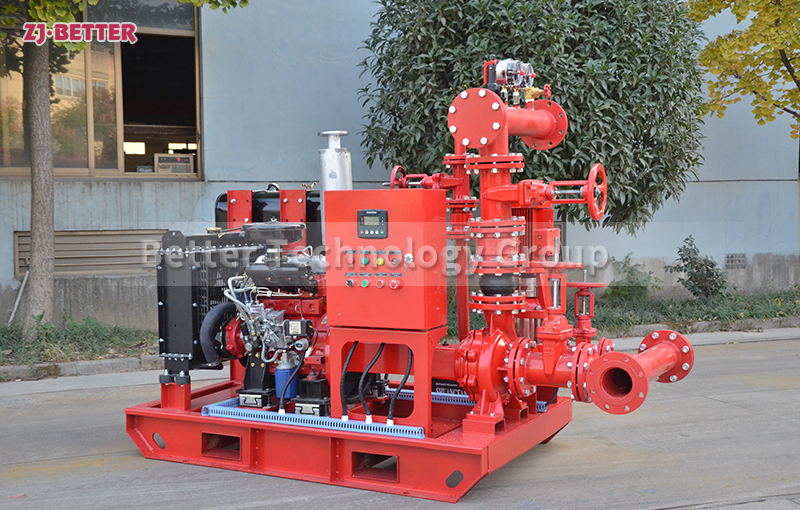
3. Choose the Right Type of Fire Pump
The most commonly used fire pump types include:
-
Horizontal Split Case Pump: Reliable and easy to maintain; ideal for larger commercial buildings.
-
Vertical Inline Pump: Space-saving and simple to install for smaller buildings.
-
End Suction Pump: Cost-effective for low-flow applications.
-
Vertical Turbine Pump: Best for underground water sources or when suction lift is required.
Your choice will depend on space, capacity, and ease of maintenance.
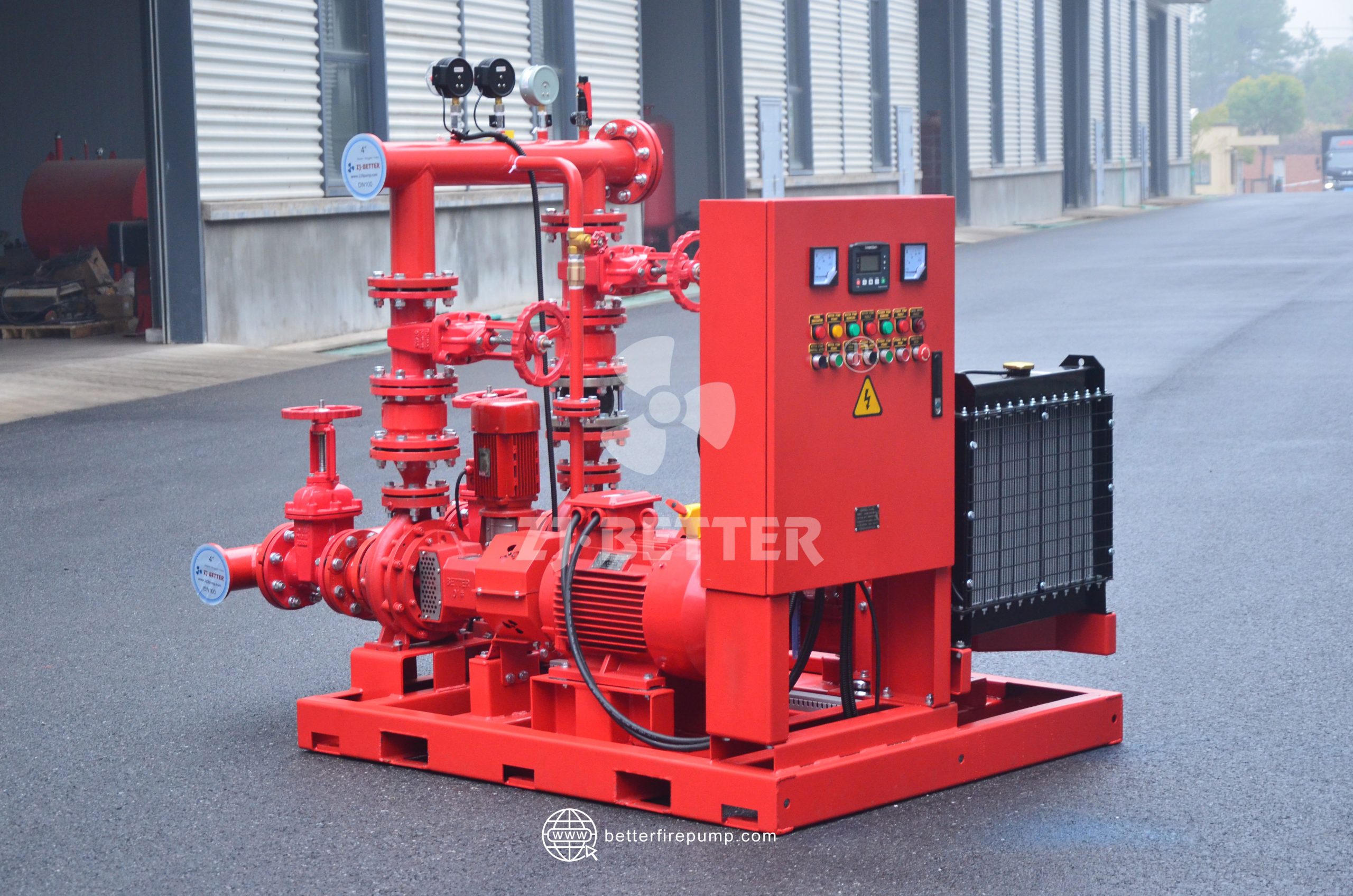
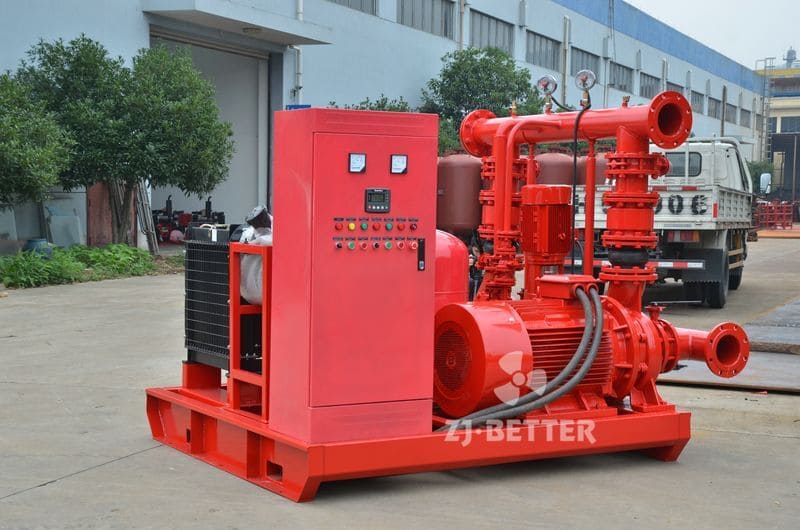
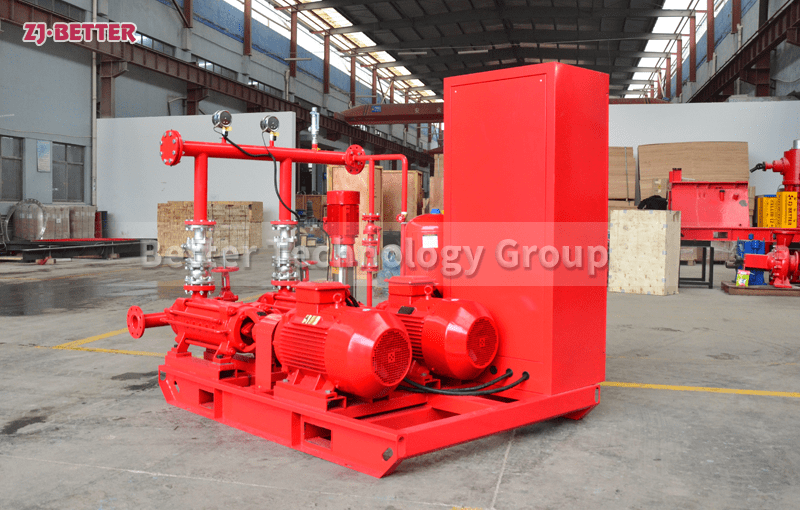
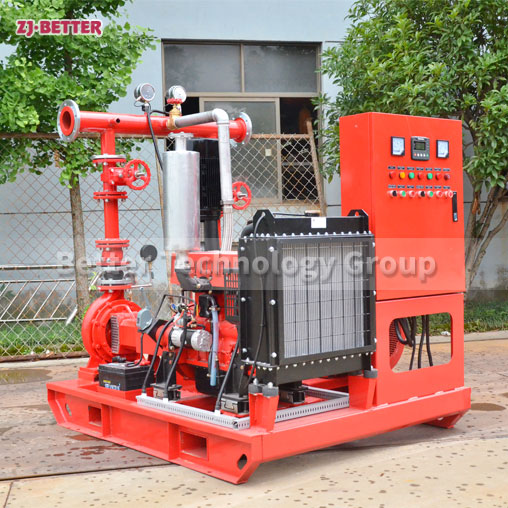
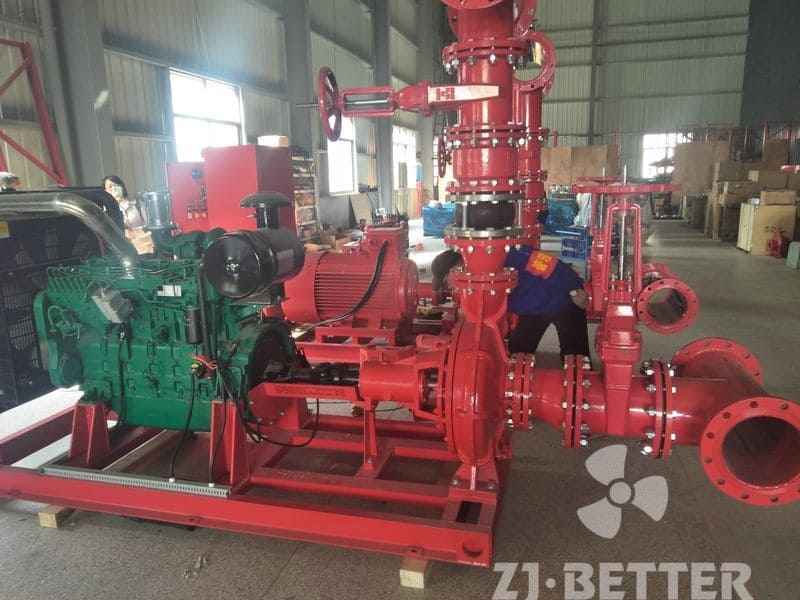
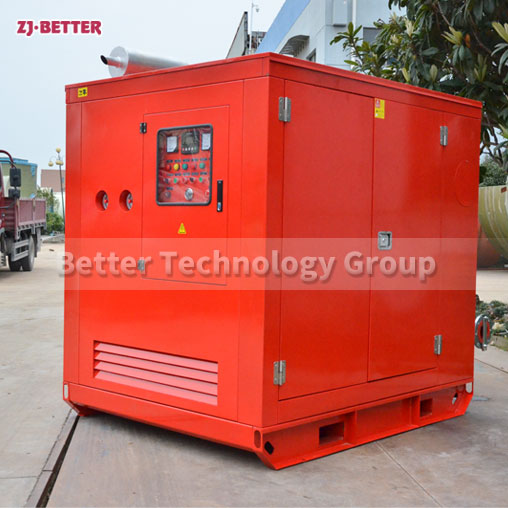
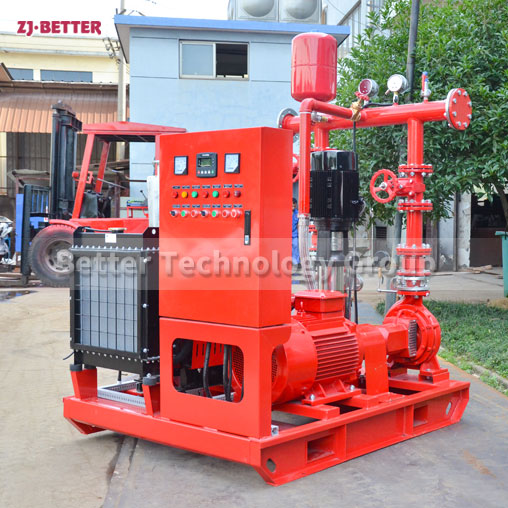
4. Select the Power Source: Electric or Diesel
Both electric motor and diesel engine fire pumps are acceptable under NFPA 20. Choose based on:
-
Electric Motor: Lower maintenance and quieter but relies on uninterrupted power supply.
-
Diesel Engine: Independent of the grid and suitable for locations with unreliable electricity but requires regular fuel and battery checks.























管道泵(不锈钢304316L).jpg)