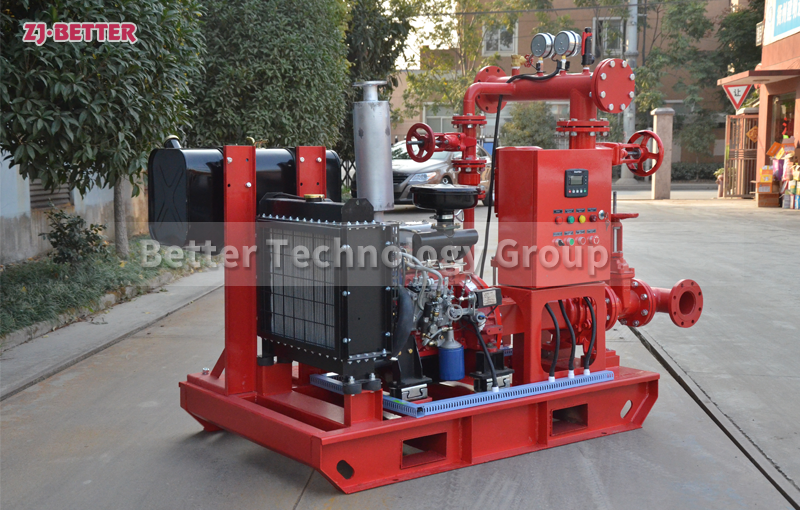
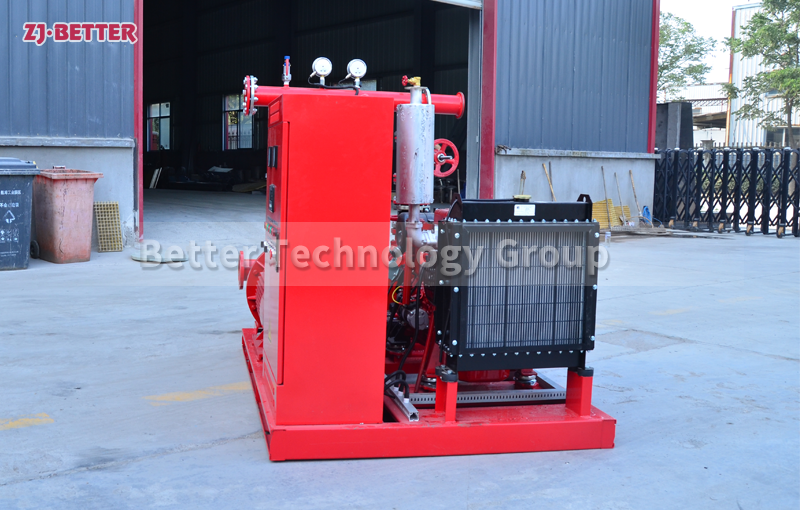
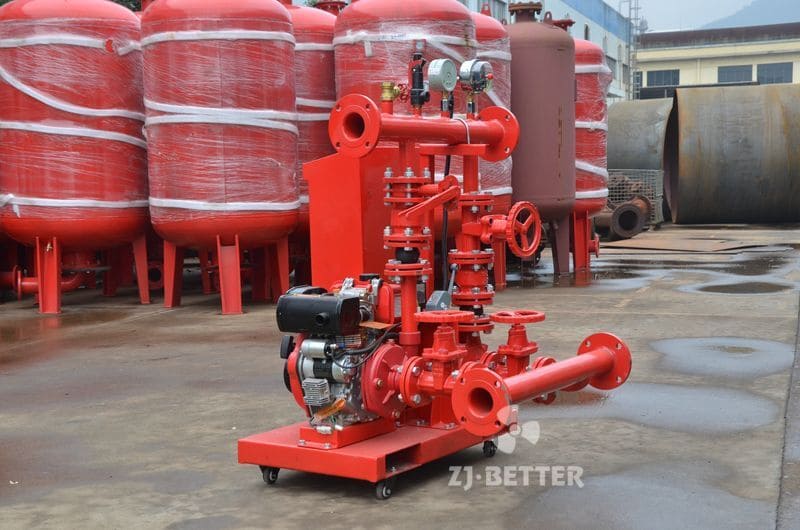
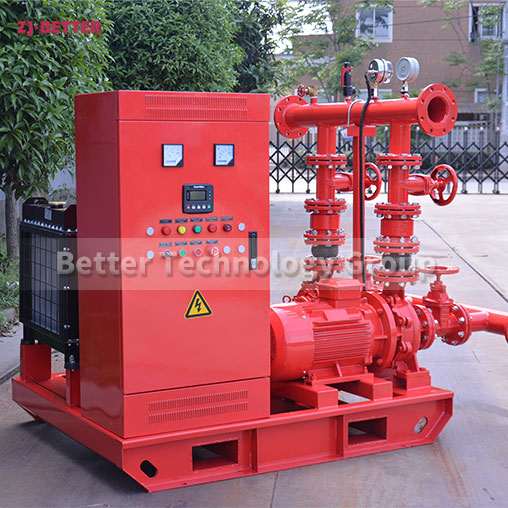
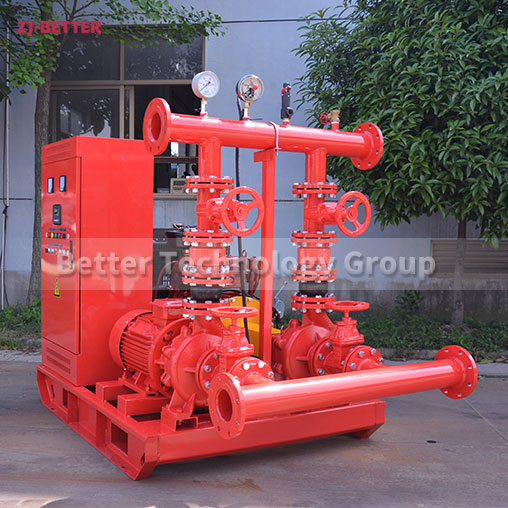
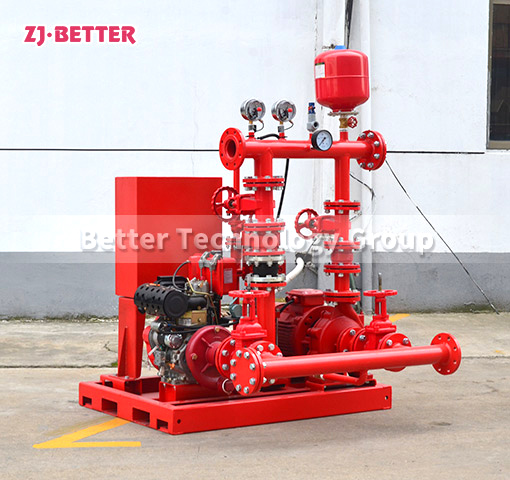
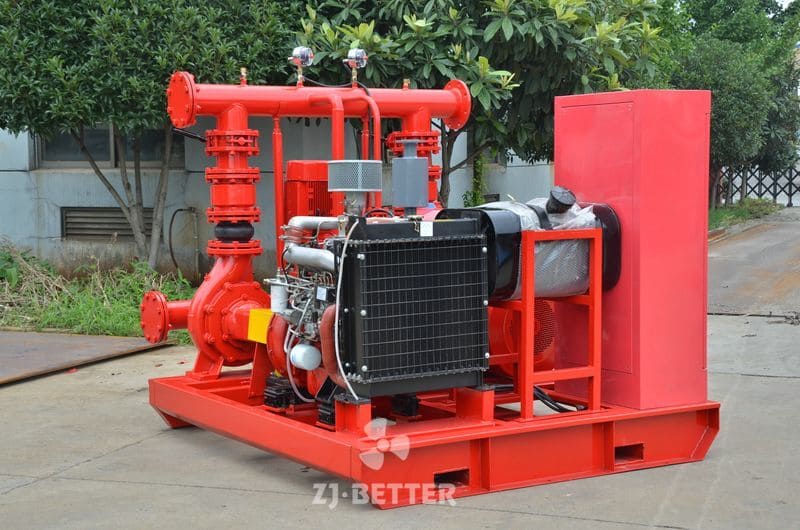
How to Prevent Fire Pump Cavitation
Learn how to prevent fire pump cavitation with proper suction design, pump sizing, and maintenance tips to protect your system and ensure reliable performance.
Cavitation is one of the most destructive issues that can affect a fire pump system. It occurs when water vapor bubbles form in the pump due to insufficient pressure at the suction side—then collapse violently, damaging internal components. If left unchecked, cavitation can lead to reduced performance, costly repairs, and even system failure during a fire emergency.
Here’s how to prevent cavitation and protect your fire pump system.
1. Understand What Causes Cavitation
Cavitation happens when the pressure at the suction side of the pump drops below the liquid’s vapor pressure, forming vapor bubbles. When these bubbles move to the high-pressure zone, they implode, causing:
-
Pitting on impellers
-
Noise and vibration
-
Decreased pump efficiency
-
Long-term mechanical damage
2. Maintain Proper Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH)
To avoid cavitation, ensure that the Net Positive Suction Head Available (NPSHA) is greater than the Net Positive Suction Head Required (NPSHR) by the pump.
Tips:
-
Reduce suction lift (the vertical distance from water source to pump)
-
Increase suction pipe diameter to reduce friction losses
-
Avoid excessive fittings and elbows before the pump
-
Ensure the water source is always filled and stable
3. Design Suction Piping Correctly
Poor suction design is one of the most common causes of cavitation.
Best Practices:
-
Keep suction piping as short and straight as possible
-
Use an eccentric reducer (flat side up) to avoid air pockets
-
Avoid elbows or valves immediately before the pump
-
Maintain a minimum of 10 pipe diameters of straight run before the pump suction flange
-
Install isolation valves only where necessary and keep them fully open during operation
4. Avoid Air Entrapment
Air in the system can drastically increase the risk of cavitation. To minimize this:
-
Ensure water tanks or reservoirs are vented properly
-
Prime the pump completely before operation
-
Inspect seals and gaskets for air leaks
-
Never allow the suction line to draw from a vortex—use a vortex suppressor if needed
5. Size the Pump Correctly
An oversized pump can pull water too aggressively from the suction line, increasing the risk of cavitation.
To avoid this:
-
Perform accurate hydraulic calculations based on system demand
-
Select a pump that operates close to its Best Efficiency Point (BEP)
-
Don’t just “oversize for safety”—oversizing can cause more harm than good
6. Monitor for Early Warning Signs
Regular inspection and testing can help detect early signs of cavitation:
-
Unusual noise (like gravel or rattling)
-
Fluctuating pressure readings
-
Drop in flow or discharge pressure
-
Vibration in the piping system
Use vibration and acoustic monitoring tools to detect issues before they become critical.
7. Follow NFPA 20 Installation Standards
NFPA 20 outlines guidelines for proper fire pump installation, including suction design and minimum NPSH requirements. Complying with these standards will significantly reduce the risk of cavitation.
Conclusion
Preventing fire pump cavitation is essential for ensuring long-term reliability and performance. Proper suction piping, accurate pump sizing, and adherence to NFPA 20 standards are key. By addressing cavitation risks proactively, you protect your investment and ensure your fire pump is always ready to perform when it matters most.