How to Select Between Electric and Diesel Fire Pumps
Discover the key differences between electric and diesel fire pumps to choose the right option based on reliability, power source, cost, and compliance.
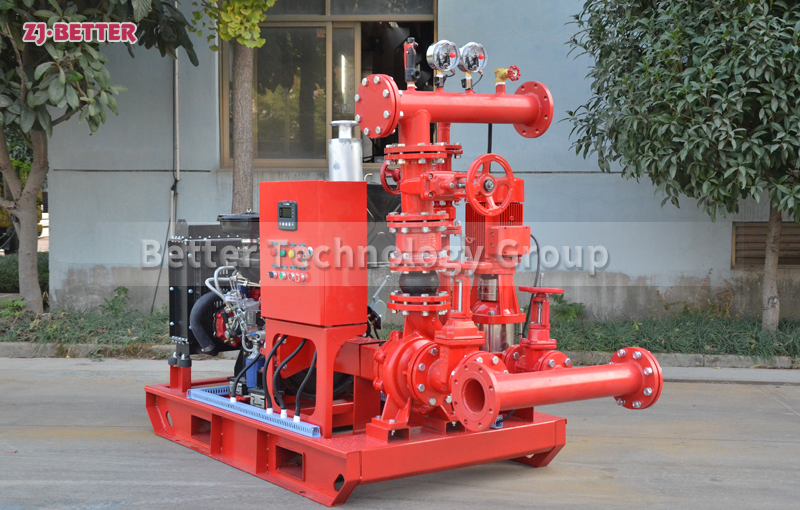
When designing a fire protection system, one of the most important decisions is choosing between an electric fire pump and a diesel fire pump. Both have their strengths and are compliant with NFPA 20 standards, but each is better suited for different environments and facility needs. This article will help you evaluate the pros and cons of each to make the best decision for your building.
1. Understand the Basic Difference
-
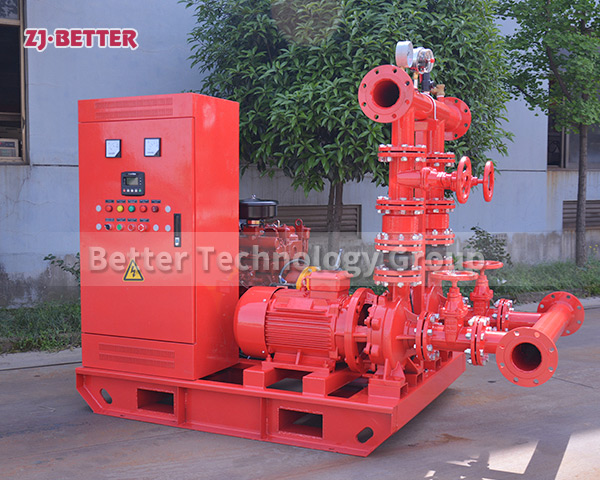
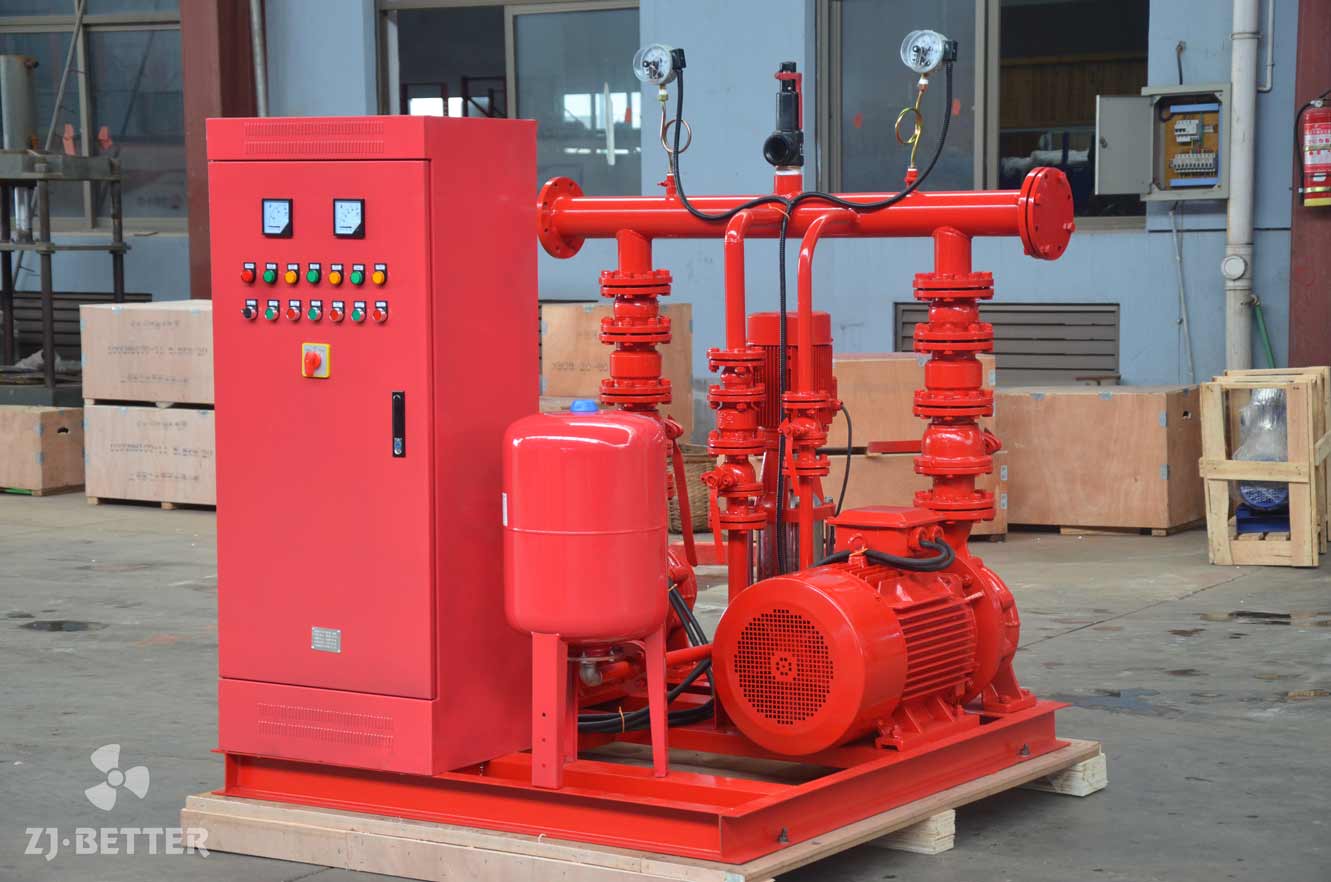
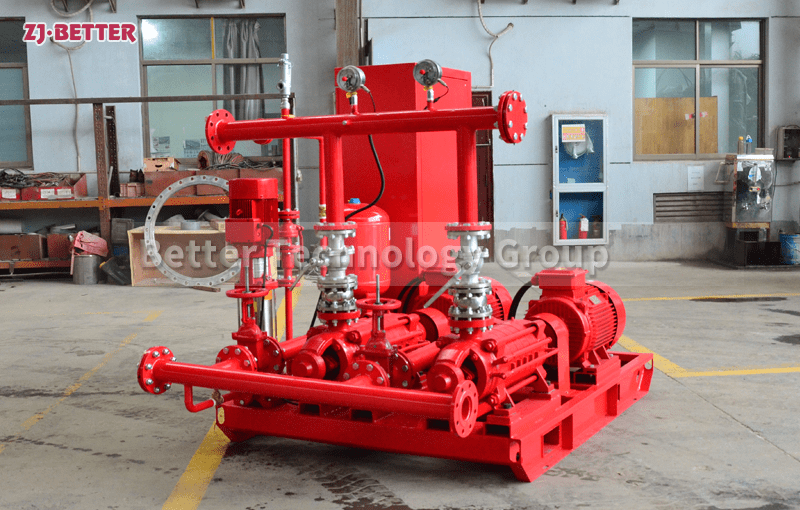
Electric Fire Pump: Powered by an electric motor connected to a reliable power source.
-
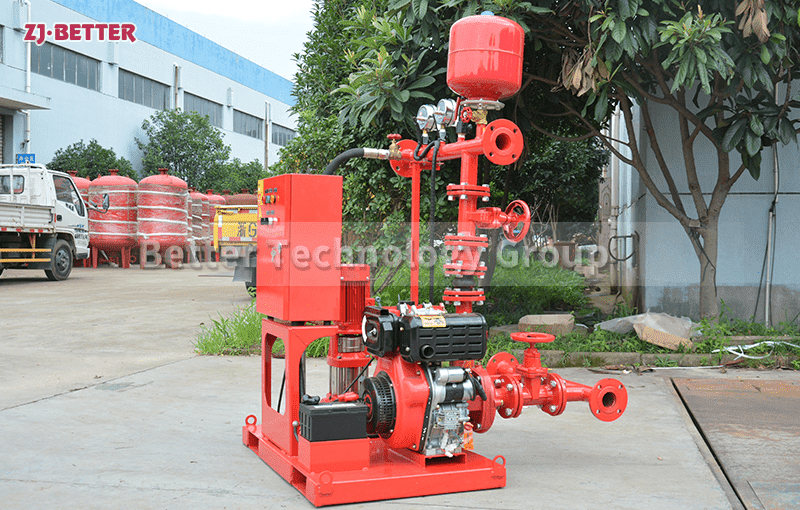
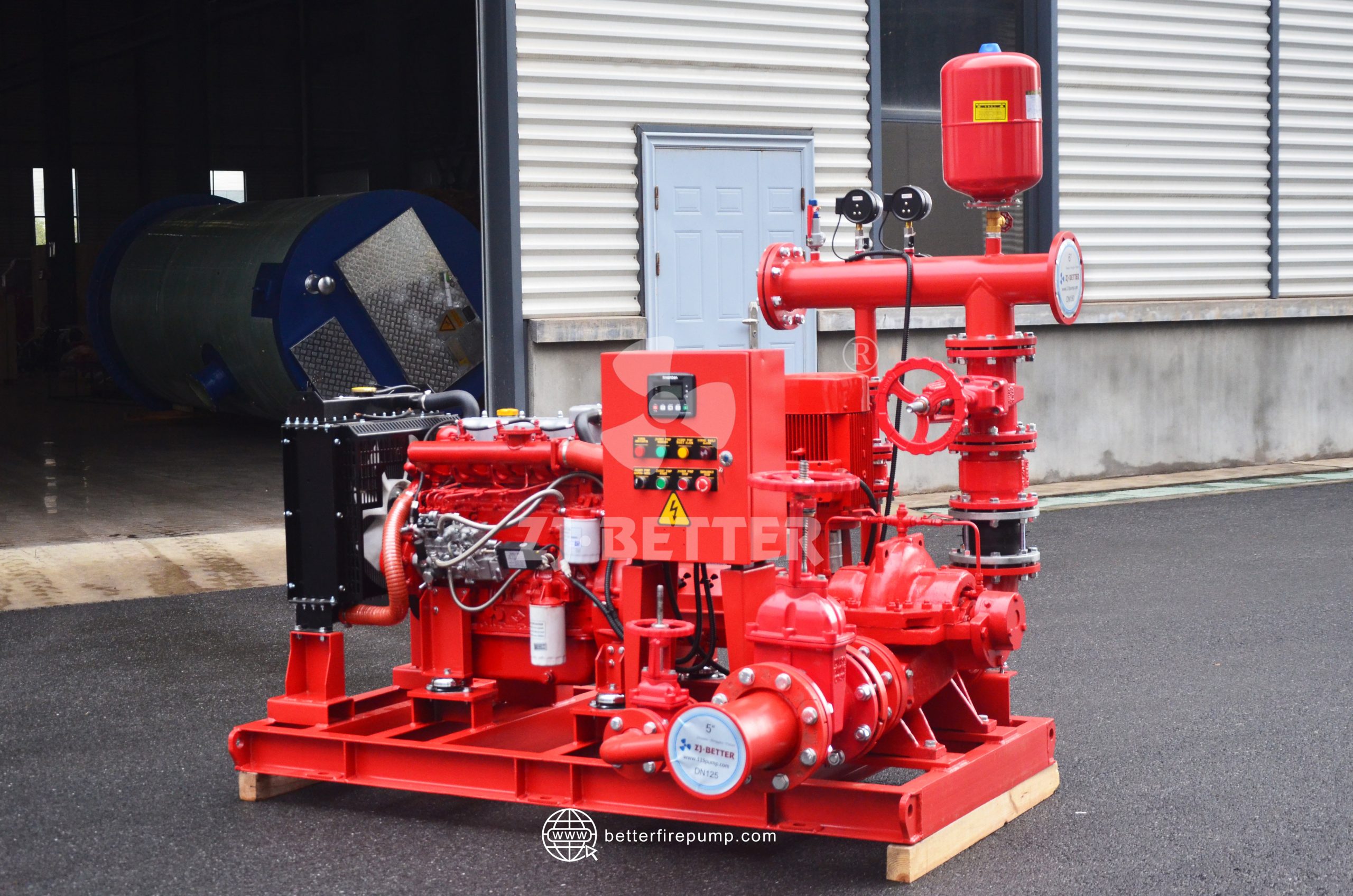
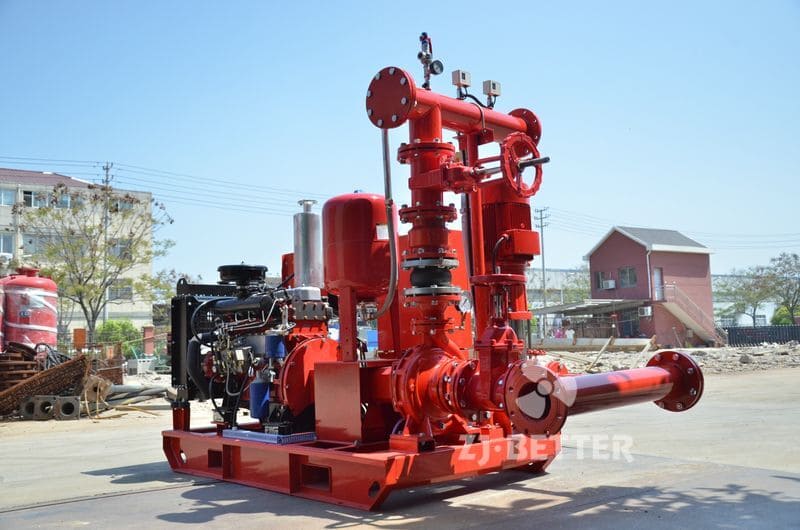
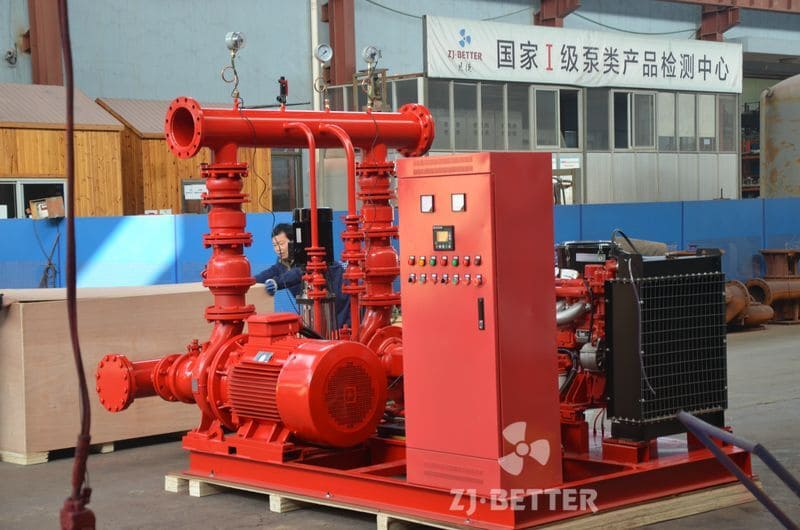
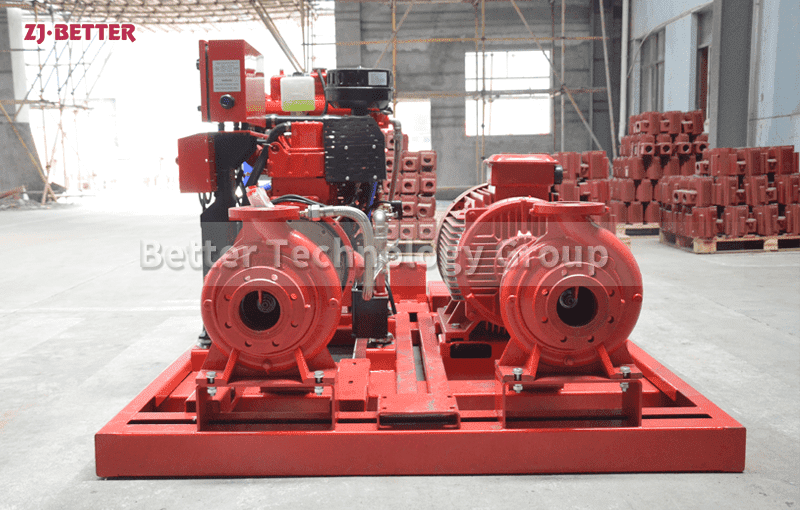
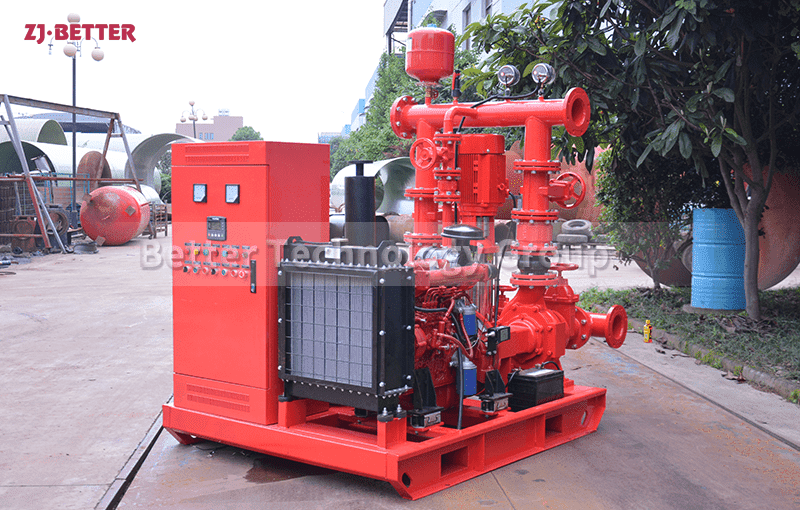
Diesel Fire Pump: Powered by a diesel engine with a fuel tank and battery system.
Both types are used in fire protection systems to ensure water is delivered at the necessary pressure and flow during an emergency.
2. Evaluate Power Supply Availability
-
If your building has a stable and reliable electrical grid, an electric fire pump is often more practical.
-
In areas prone to power outages, especially during natural disasters, a diesel fire pump offers independent operation without needing backup electricity.
According to NFPA 20, if the electric power supply is not deemed “reliable,” a backup source (like a diesel pump) must be provided.
3. Consider Installation and Operating Costs
-
Electric Pumps:
-
Lower initial cost
-
Lower maintenance and simpler setup
-
Lower noise levels
-
-
Diesel Pumps:
-
Higher initial cost (engine, tank, exhaust, etc.)
-
Requires regular fuel refills and maintenance
-
Requires more space for ventilation and fuel storage
-
Although diesel pumps may cost more, they are necessary in many critical applications where electrical reliability cannot be guaranteed.
4. Review Space and Ventilation Needs
-
Electric fire pumps are compact and require less mechanical infrastructure.
-
Diesel fire pumps need more space for:
-
Fuel storage
-
Engine ventilation
-
Exhaust routing
-
Battery charging stations
-
This can affect building layout, especially in tight pump rooms or retrofitted buildings.
5. Assess Maintenance Requirements
-
Electric motors have fewer moving parts and require less frequent maintenance.
-
Diesel engines need:
-
Regular fuel checks
-
Battery inspections
-
Oil and coolant replacement
-
Monthly and annual engine tests
-
Facility teams must be trained to maintain diesel systems properly.
6. Check Compliance and Local Code Requirements
Some jurisdictions mandate diesel pumps in specific building types (e.g., hospitals, data centers, high-rises) where emergency readiness is critical. Always consult with:
-
Local fire protection engineers
-
AHJ (Authority Having Jurisdiction)
-
NFPA 20 guidelines
7. Use Cases and Recommendations
| Building Type | Recommended Fire Pump |
|---|---|
| Urban Office Building | Electric (if reliable grid) |
| Remote Industrial Facility | Diesel (power may be unreliable) |
| Hospital or Data Center | Diesel or Dual Power Source |
| Shopping Mall with Generator | Electric + Generator backup |
Conclusion
Choosing between electric and diesel fire pumps is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It depends on your power infrastructure, budget, building layout, and compliance requirements. Understanding the advantages of each option will help you make an informed, code-compliant, and reliable choice for your fire protection system.